Differential gating and recruitment of P/Q-, N-, and R-type Ca2+ channels in hippocampal mossy fiber boutons
- PMID: 18057200
- PMCID: PMC6673086
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1709-07.2007
Differential gating and recruitment of P/Q-, N-, and R-type Ca2+ channels in hippocampal mossy fiber boutons
Abstract
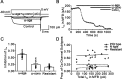
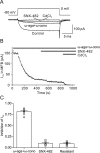
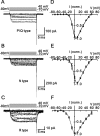
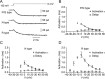
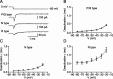
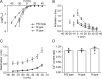
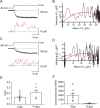
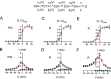
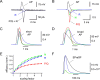
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in presynaptic terminals initiate the Ca2+ inflow necessary for transmitter release. At a variety of synapses, multiple Ca2+ channel subtypes are involved in synaptic transmission and plasticity. However, it is unknown whether presynaptic Ca2+ channels differ in gating properties and whether they are differentially activated by action potentials or subthreshold voltage signals. We examined Ca2+ channels in hippocampal mossy fiber boutons (MFBs) by presynaptic recording, using the selective blockers omega-agatoxin IVa, omega-conotoxin GVIa, and SNX-482 to separate P/Q-, N-, and R-type components. Nonstationary fluctuation analysis combined with blocker application revealed a single MFB contained on average approximately 2000 channels, with 66% P/Q-, 26% N-, and 8% R-type channels. Whereas both P/Q-type and N-type Ca2+ channels showed high activation threshold and rapid activation and deactivation, R-type Ca2+ channels had a lower activation threshold and slower gating kinetics. To determine the efficacy of activation of different Ca2+ channel subtypes by physiologically relevant voltage waveforms, a six-state gating model reproducing the experimental observations was developed. Action potentials activated P/Q-type Ca2+ channels with high efficacy, whereas N- and R-type channels were activated less efficiently. Action potential broadening selectively recruited N- and R-type channels, leading to an equalization of the efficacy of channel activation. In contrast, subthreshold presynaptic events activated R-type channels more efficiently than P/Q- or N-type channels. In conclusion, single MFBs coexpress multiple types of Ca2+ channels, which are activated differentially by subthreshold and suprathreshold presynaptic voltage signals.
Figures
References
-
- Alle H, Geiger JRP. Combined analog and action potential coding in hippocampal mossy fibers. Science. 2006;311:1290–1293. - PubMed
-
- Arikkath J, Campbell KP. Auxiliary subunits: essential components of the voltage-gated calcium channel complex. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:298–307. - PubMed
-
- Awatramani GB, Price GD, Trussell LO. Modulation of transmitter release by presynaptic resting potential and background calcium levels. Neuron. 2005;48:109–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
