Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces cellular MicroRNA miR-146a, a modulator of lymphocyte signaling pathways
- PMID: 18057241
- PMCID: PMC2258704
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02136-07
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces cellular MicroRNA miR-146a, a modulator of lymphocyte signaling pathways
Abstract
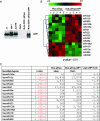
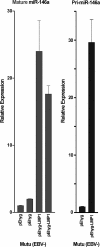
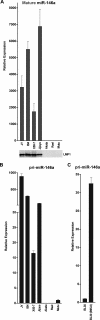
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is a functional homologue of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family and contributes substantially to the oncogenic potential of EBV through activation of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB). MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small RNA molecules that are involved in the regulation of cellular processes such as growth, development, and apoptosis and have recently been linked to cancer phenotypes. Through miRNA microarray analysis, we demonstrate that LMP1 dysregulates the expression of several cellular miRNAs, including the most highly regulated of these, miR-146a. Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR analysis confirmed induced expression of miR-146a by LMP1. Analysis of miR-146a expression in EBV latency type III and type I cell lines revealed substantial expression of miR-146a in type III (which express LMP1) but not in type I cell lines. Reporter studies demonstrated that LMP1 induces miR-146a predominantly through two NF-kappaB binding sites in the miR-146a promoter and identified a role for an Oct-1 site in conferring basal and induced expression. Array analysis of cellular mRNAs expressed in Akata cells transduced with an miR-146a-expressing retrovirus identified genes that are directly or indirectly regulated by miR-146a, including a group of interferon-responsive genes that are inhibited by miR-146a. Since miR-146a is known to be induced by agents that activate the interferon response pathway (including LMP1), these results suggest that miR-146a functions in a negative feedback loop to modulate the intensity and/or duration of the interferon response.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) induces the expression of the cellular microRNA miR-146a.RNA Biol. 2007 Nov;4(3):131-7. doi: 10.4161/rna.4.3.5206. RNA Biol. 2007. PMID: 18347435
-
NF-κB Signaling Regulates Expression of Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.J Virol. 2016 Jun 24;90(14):6475-88. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00613-16. Print 2016 Jul 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27147748 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 trans-activates miR-155 transcription through the NF-kappaB pathway.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Nov;36(20):6608-19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn666. Epub 2008 Oct 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18940871 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
The Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:119-49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428373 Review.
Cited by
-
Looking at Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Host Interactions from a microRNA Viewpoint.Front Microbiol. 2012 Jan 11;2:271. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00271. eCollection 2011. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22275910 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of microRNA-146a and microRNA-181b in regulating the secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β in silicon dioxide-induced NR8383 rat macrophages.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Oct;12(4):5587-93. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4083. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26239160 Free PMC article.
-
Particulate Air Pollution Exposure and Expression of Viral and Human MicroRNAs in Blood: The Beijing Truck Driver Air Pollution Study.Environ Health Perspect. 2016 Mar;124(3):344-50. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1408519. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Environ Health Perspect. 2016. PMID: 26068961 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Innate Immunity by microRNAs.Antibodies (Basel). 2016 Apr 1;5(2):8. doi: 10.3390/antib5020008. Antibodies (Basel). 2016. PMID: 31557989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA signatures associated with immortalization of EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines and their clinical traits.Cell Prolif. 2011 Feb;44(1):59-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2010.00717.x. Cell Prolif. 2011. PMID: 21199010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira, S., and K. Takeda. 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4499-511. - PubMed
-
- Bolstad, B. M., R. A. Irizarry, M. Astrand, and T. P. Speed. 2003. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 19185-193. - PubMed
-
- Brodeur, S. R., G. Cheng, D. Baltimore, and D. A. Thorley-Lawson. 1997. Localization of the major NF-κB-activating site and the sole TRAF3 binding site of LMP-1 defines two distinct signaling motifs. J. Biol. Chem. 27219777-19784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

