Immunotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer with vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage-activating factor, GcMAF
- PMID: 18058096
- PMCID: PMC11031063
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-007-0431-z
Immunotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer with vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage-activating factor, GcMAF
Retraction in
-
Retraction note to: immunotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer with vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage-activating factor, GcMAF.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014 Dec;63(12):1349. doi: 10.1007/s00262-014-1616-x. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25297451 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
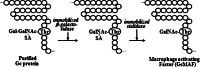
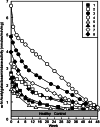
Serum vitamin D binding protein (Gc protein) is the precursor for the principal macrophage-activating factor (MAF). The MAF precursor activity of serum Gc protein of colorectal cancer patients was lost or reduced because Gc protein is deglycosylated by serum alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase (Nagalase) secreted from cancerous cells. Deglycosylated Gc protein cannot be converted to MAF, leading to immunosuppression. Stepwise treatment of purified Gc protein with immobilized beta-galactosidase and sialidase generated the most potent macrophage-activating factor (GcMAF) ever discovered, but it produces no side effect in humans. Macrophages treated with GcMAF (100 microg/ml) develop an enormous variation of receptors and are highly tumoricidal to a variety of cancers indiscriminately. Administration of 100 nanogram (ng)/ human maximally activates systemic macrophages that can kill cancerous cells. Since the half-life of the activated macrophages is approximately 6 days, 100 ng GcMAF was administered weekly to eight nonanemic colorectal cancer patients who had previously received tumor-resection but still carried significant amounts of metastatic tumor cells. As GcMAF therapy progressed, the MAF precursor activities of all patients increased and conversely their serum Nagalase activities decreased. Since serum Nagalase is proportional to tumor burden, serum Nagalase activity was used as a prognostic index for time course analysis of GcMAF therapy. After 32-50 weekly administrations of 100 ng GcMAF, all colorectal cancer patients exhibited healthy control levels of the serum Nagalase activity, indicating eradication of metastatic tumor cells. During 7 years after the completion of GcMAF therapy, their serum Nagalase activity did not increase, indicating no recurrence of cancer, which was also supported by the annual CT scans of these patients.
Figures

Comment in
-
Inconsistencies and questionable reliability of the publication "immunotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer with vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophages-activating, GcMAF" by Yamamoto et al.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014 Dec;63(12):1347-8. doi: 10.1007/s00262-014-1587-y. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25056820 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Immunotherapy of metastatic breast cancer patients with vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage activating factor (GcMAF).Int J Cancer. 2008 Jan 15;122(2):461-7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23107. Int J Cancer. 2008. Retraction in: Int J Cancer. 2014 Sep 15;135(6):1509. PMID: 17935130 Retracted.
-
Immunotherapy of HIV-infected patients with Gc protein-derived macrophage activating factor (GcMAF).J Med Virol. 2009 Jan;81(1):16-26. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21376. J Med Virol. 2009. Retraction in: J Med Virol. 2014 Nov;86(11):1998. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24060. PMID: 19031451 Retracted.
-
Immunotherapy for Prostate Cancer with Gc Protein-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor, GcMAF.Transl Oncol. 2008 Jul;1(2):65-72. doi: 10.1593/tlo.08106. Transl Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18633461 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy with GcMAF revisited - A critical overview of the research of Nobuto Yamamoto.Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2022;31:100537. doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2022.100537. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 35217488 Review.
-
Is α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase the key to curing cancer? A mini-review and hypothesis.J BUON. 2017 Nov-Dec;22(6):1372-1377. J BUON. 2017. PMID: 29332325 Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated urinary level of vitamin D-binding protein as a novel biomarker for diabetic nephropathy.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Feb;7(2):411-416. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.1426. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 24396416 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating vitamin D binding protein, total, free and bioavailable 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of colorectal cancer.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 22;5:7956. doi: 10.1038/srep07956. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25609140 Free PMC article.
-
GC protein-derived macrophage-activating factor decreases α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase levels in advanced cancer patients.Oncoimmunology. 2013 Aug 1;2(8):e25769. doi: 10.4161/onci.25769. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Oncoimmunology. 2013. PMID: 24179708 Free PMC article.
-
Inconsistencies and questionable reliability of the publication "immunotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer with vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophages-activating, GcMAF" by Yamamoto et al.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014 Dec;63(12):1347-8. doi: 10.1007/s00262-014-1587-y. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25056820 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Vitamin D Binding Protein: A Historic Overview.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Jan 10;10:910. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00910. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 31998239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cohen AM, Shank B, Friedman MA. Colorectal cancer. In: Devita VT Jr, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editors. Cancer, principle and practice of oncology, 3. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott; 1989. pp. 895–964.
-
- Gleason DF. The Veteran,s Administration Cooperative Urological Research Group: histological grading and clinical staging of prostate carcinoma. In: Tannenbaum M, editor. Urologic pathology: the prostate. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger; 1977. pp. 171–198.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

