In vivo gene silencing identifies the Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteasome as essential for the bacteria to persist in mice
- PMID: 18059281
- PMCID: PMC3174471
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1683
In vivo gene silencing identifies the Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteasome as essential for the bacteria to persist in mice
Abstract
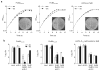
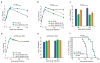
The success of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) as a human pathogen relies on its ability to resist eradication by the immune system. The identification of mechanisms that enable Mtb to persist is key for finding ways to limit latent tuberculosis, which affects one-third of the world's population. Here we show that conditional gene silencing can be used to determine whether an Mtb gene required for optimal growth in vitro is also important for virulence and, if so, during which phase of an infection it is required. Application of this approach to the prcBA genes, which encode the core of the mycobacterial proteasome, revealed an unpredicted requirement of the core proteasome for the persistence of Mtb during the chronic phase of infection in mice. Proteasome depletion also attenuated Mtb in interferon-gamma-deficient mice, pointing to a function of the proteasome beyond defense against the adaptive immune response. Genes that are essential for growth in vitro, in vivo or both account for approximately 20% of Mtb's genome. Conditional gene silencing could therefore facilitate the validation of up to 800 potential Mtb drug targets and improve our understanding of host-pathogen dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Corbett EL, et al. The growing burden of tuberculosis: global trends and interactions with the HIV epidemic. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:1009–21. - PubMed
-
- Gomez JE, McKinney JDM. tuberculosis persistence, latency, and drug tolerance. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2004;84:29–44. - PubMed
-
- McKinney JD, et al. Persistence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in macrophages and mice requires the glyoxylate shunt enzyme isocitrate lyase. Nature. 2000;406:735–8. - PubMed
-
- Glickman MS, Cox JS, Jacobs WR., Jr A novel mycolic acid cyclopropane synthetase is required for cording, persistence, and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mol Cell. 2000;5:717–27. - PubMed
-
- Stewart GR, et al. Overexpression of heat-shock proteins reduces survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the chronic phase of infection. Nat Med. 2001;7:732–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

