Effects of zileuton and montelukast in mouse experimental spinal cord injury
- PMID: 18059327
- PMCID: PMC2241786
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707577
Effects of zileuton and montelukast in mouse experimental spinal cord injury
Abstract
Background and purpose: 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) is the key enzyme in leukotriene (LT) biosynthesis from arachidonic acid (AA). Here, we examined the role of the 5-LO-product, cysteinyl-LT (Cys-LT), with a 5-LO inhibitor (zileuton) and a Cys-LT, receptor antagonist (montelukast), in the inflammatory response and tissue injury associated with spinal cord injury (SCI).
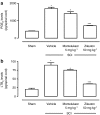
Experimental approach: SCI was induced in mice by the application of vascular clips to the dura via a two-level T6 to T7 laminectomy for 1 min. Cord inflammation was assessed histologically and by measuring inflammatory mediators (ELISA) and apoptosis by annexin V, TUNEL, Fas ligand staining and Bax and Bcl-2 expression (immunohistochemistry and western blots). Motor function in hindlimbs was assessed by a locomotor rating scale, for 10 days after cord injury.
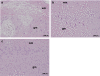
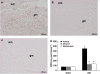
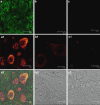
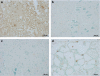
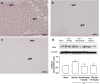
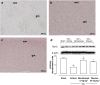
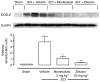
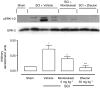
Key results: SCI in mice resulted in tissue damage, oedema, neutrophil infiltration, apoptosis, tumour necrosis-alpha (TNF-alpha) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression, prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) and leukotriene B(4) (LTB(4)) production, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation in injured tissue. Treatment of the mice with zileuton or montelukast reduced the spinal cord inflammation and tissue injury, neutrophil infiltration, TNF-alpha, COX-2 and pERK1/2 expression, PGE(2) and LTB(4) production, and apoptosis. In separate experiments, zileuton or montelukast significantly improved the recovery of limb function over 10 days.
Conclusions and implications: Zileuton and montelukast produced a substantial reduction of inflammatory events associated with experimental SCI. Our data underline the important role of 5-LO and Cys-LT in neurotrauma.
Figures
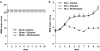
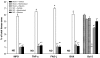


References
-
- Adachi K, Yimin Y, Satake K, Matsuyama Y, Ishiguro N, Sawada M, et al. Localization of cyclooxygenase-2 induced following traumatic spinal cord injury. Neurosci Res. 2005;51:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Anderson AJ. Mechanisms and pathways of inflammatory responses in CNS trauma: spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. 2002;25:70–79. - PubMed
-
- Bao F, Chen Y, Dekaban GA, Weaver LC. An anti-CD11d integrin antibody reduces cyclooxygenase-2 expression and protein and DNA oxidation after spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurochem. 2004;90:1194–1204. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Peled O, Knudson M, Korsmeyer SJ, Rothstein JD. Motor neuron degeneration is attenuated in Bax-deficient neurons in vitro. J Neurosci Res. 1999;55:542–556. - PubMed
-
- Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12:1–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

