Role of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor at glutamatergic synapses
- PMID: 18059328
- PMCID: PMC2268077
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707509
Role of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor at glutamatergic synapses
Abstract
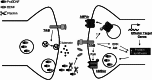
The neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) plays an important role in the activity-dependent regulation of synaptic structure and function, particularly of the glutamatergic synapses. BDNF may be released in the mature form, which activates preferentially TrkB receptors, or as proBDNF, which is coupled to the stimulation of the p75(NTR). In the mature form BDNF induces rapid effects on glutamate release, and may induce short- and long-term effects on the postsynaptic response to the neurotransmitter. BDNF may affect glutamate receptor activity by inducing the phosphorylation of the receptor subunits, which may also affect the interaction with intracellular proteins and, consequently, their recycling and localization to defined postsynaptic sites. Stimulation of the local protein synthesis and transcription activity account for the delayed effects of BDNF on glutamatergic synaptic strength. Several evidences show impaired synaptic plasticity of glutamatergic synapses in diseases where compromised BDNF function has been observed, such as Huntington's disease, depression, anxiety, and the BDNF polymorphism Val66Met, suggesting that upregulating BDNF-activated pathways may be therapeutically relevant. This review focuses on recent advances in the understanding of the regulation of the glutamatergic synapse by BDNF, and its implications in synaptic plasticity.
Figures
References
-
- Aakalu G, Smith WB, Nguyen N, Jiang C, Schuman EM. Dynamic visualization of local protein synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 2001;30:489–502. - PubMed
-
- Abidin I, Kohler T, Weiler E, Zoidl G, Eysel UT, Lessmann V, et al. Reduced presynaptic efficiency of excitatory synaptic transmission impairs LTP in the visual cortex of BDNF-heterozygous mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;24:3519–3531. - PubMed
-
- Almeida RD, Manadas BJ, Melo CV, Gomes JR, Mendes CS, Graos MM, et al. Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12:1329–1343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

