Urinary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury
- PMID: 18059454
- PMCID: PMC2586909
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002715
Urinary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury
Erratum in
- Kidney Int. 2009 Aug;76(3):348-9
Abstract
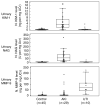
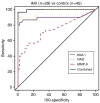
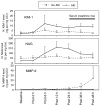
A change in the serum creatinine is not sensitive for an early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. We evaluated urinary levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG), and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) as biomarkers for the detection of acute kidney injury. Urine samples were collected from 44 patients with various acute and chronic kidney diseases, and from 30 normal subjects in a cross-sectional study. A case-control study of children undergoing cardio-pulmonary bypass surgery included urine specimens from each of 20 patients without and with acute kidney injury. Injury was defined as a greater than 50% increase in the serum creatinine within the first 48 h after surgery. The biomarkers were normalized to the urinary creatinine concentration at 12, 24, and 36 h after surgery with the areas under the receiver-operating characteristic curve compared for performance. In the cross-sectional study, the area under the curve for MMP-9 was least sensitive followed by KIM-1 and NAG. Combining all three biomarkers achieved a perfect score diagnosing acute kidney injury. In the case-control study, KIM-1 was better than NAG at all time points, but combining both was no better than KIM-1 alone. Urinary MMP-9 was not a sensitive marker in the case-control study. Our results suggest that urinary biomarkers allow diagnosis of acute kidney injury earlier than a rise in serum creatinine.
Figures
Comment on
-
Acute kidney injury: Better biomarkers and beyond.Kidney Int. 2008 Apr;73(7):801-3. doi: 10.1038/ki.2008.17. Kidney Int. 2008. PMID: 18340352 Review.
Similar articles
-
Urinary biomarkers in the early detection of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 May;4(5):873-82. doi: 10.2215/CJN.04810908. Epub 2009 Apr 30. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19406962 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary N-acetyl-beta-(D)-glucosaminidase activity and kidney injury molecule-1 level are associated with adverse outcomes in acute renal failure.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007 Mar;18(3):904-12. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006030221. Epub 2007 Jan 31. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17267747
-
Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 are noninvasive biomarkers of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in lung cancer patients.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;76(5):989-96. doi: 10.1007/s00280-015-2880-y. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26407820 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Urinary and serum biomarkers for the diagnosis of acute kidney injury: an in-depth review of the literature.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Feb;28(2):254-73. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs380. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23115326 Review.
-
Diagnosis of acute kidney injury: from classic parameters to new biomarkers.Contrib Nephrol. 2007;156:213-9. doi: 10.1159/000102086. Contrib Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17464130 Review.
Cited by
-
The Assessment of the Usefulness of Selected Markers in the Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease in Children.Biomark Insights. 2021 Apr 20;16:11772719211011173. doi: 10.1177/11772719211011173. eCollection 2021. Biomark Insights. 2021. PMID: 33958853 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein as a predictor of ESRD and CVD in patients with CKD.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016 Apr;20(2):195-203. doi: 10.1007/s10157-015-1144-9. Epub 2015 Jul 19. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26189083
-
Are endourological procedures for nephrolithiasis treatment associated with renal injury? A review of potential mechanisms and novel diagnostic indexes.Clin Kidney J. 2020 May 22;13(4):531-541. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa020. eCollection 2020 Aug. Clin Kidney J. 2020. PMID: 32905259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Childhood Obesity: Insight into Kidney Involvement.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 12;24(24):17400. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417400. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) mediates renal epithelial cell repair via ERK MAPK signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 May;416(1-2):109-16. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2700-7. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27084535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Star RA. Treatment of acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1998;54:1817–1831. - PubMed
-
- Han WK, Bonventre JV. Biologic markers for the early detection of acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2004;10:476–482. - PubMed
-
- Ichimura T, Bonventre JV, Bailly V, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is upregulated in renal cells after injury. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:4135–4142. - PubMed
-
- Han WK, Bailly V, Abichandani R, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int. 2002;62:237–244. - PubMed
-
- Ichimura T, Hung CC, Yang SA, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1: a tissue and urinary biomarker for nephrotoxicant-induced renal injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004;286:F552–F563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 DK075941/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK074099/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK072381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK53289/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK074099/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK039773/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053289/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK39773/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R33 DK074099/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK064075/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- KO8-DK64075/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

