Potentiation of Excitotoxicity in HIV-1 Associated Dementia and the Significance of Glutaminase
- PMID: 18059978
- PMCID: PMC1832112
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cnr.2006.09.009
Potentiation of Excitotoxicity in HIV-1 Associated Dementia and the Significance of Glutaminase
Abstract
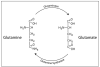
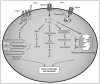
HIV-1 Associated Dementia (HAD) is a significant consequence of HIV infection. Although multiple inflammatory factors contribute to this chronic, progressive dementia, excitotoxic damage appears to be an underlying mechanism in the neurodegenerative process. Excitotoxicity is a cumulative effect of multiple processes occurring in the CNS during HAD. The overstimulation of glutamate receptors, an increased vulnerability of neurons, and disrupted astrocyte support each potentiate excitotoxic damage to neurons. Recent evidence suggests that poorly controlled generation of glutamate by phosphate-activated glutaminase may contribute to the neurotoxic state typical of HAD as well as other neurodegenerative disorders. Glutaminase converts glutamine, a widely available substrate throughout the CNS to glutamate. Inflammatory conditions may precipitate unregulated activity of glutaminase, a potentially important mechanism in HAD pathogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vitro glutaminase regulation and mechanisms of glutamate generation in HIV-1-infected macrophage.J Neurochem. 2009 Apr;109(2):551-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.05989.x. Epub 2009 Feb 13. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19222703 Free PMC article.
-
Increased production of extracellular glutamate by the mitochondrial glutaminase following neuronal death.J Biol Chem. 1997 Apr 25;272(17):11276-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.17.11276. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9111031
-
Mitochondrial glutaminase enhances extracellular glutamate production in HIV-1-infected macrophages: linkage to HIV-1 associated dementia.J Neurochem. 2004 Jan;88(1):169-80. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02146.x. J Neurochem. 2004. PMID: 14675161
-
Regulated expression of sodium-dependent glutamate transporters and synthetase: a neuroprotective role for activated microglia and macrophages in HIV infection?Brain Pathol. 2003 Apr;13(2):211-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2003.tb00020.x. Brain Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12744474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory mediators leading to protein misfolding and uncompetitive/fast off-rate drug therapy for neurodegenerative disorders.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2007;82:1-27. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(07)82001-0. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17678953 Review.
Cited by
-
Nicotine attenuates the effect of HIV-1 proteins on the neural circuits of working and contextual memories.Mol Brain. 2015 Jul 24;8:43. doi: 10.1186/s13041-015-0134-x. Mol Brain. 2015. PMID: 26205781 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of ephrin receptors and ligands in postmortem brains of HIV-infected subjects with and without cognitive impairment.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;8(1):333-44. doi: 10.1007/s11481-012-9429-1. Epub 2013 Jan 12. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23314923 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-gated potassium channels in human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1)-associated neurocognitive disorders.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009 Mar;4(1):60-70. doi: 10.1007/s11481-008-9106-6. Epub 2008 May 6. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18459047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutaminase C overexpression in the brain induces learning deficits, synaptic dysfunctions, and neuroinflammation in mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2017 Nov;66:135-145. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.06.007. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Brain Behav Immun. 2017. PMID: 28624534 Free PMC article.
-
A coat of many colors: neuroimmune crosstalk in human immunodeficiency virus infection.Neuron. 2009 Oct 15;64(1):133-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.09.042. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19840555 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Piot P, Bartos M, Ghys PD, Walker N, Schwartlander B. The global impact of HIV/AIDS. Nature. 2001 Apr 19;410(6831):968–73. - PubMed
-
- McArthur JC. Neurologic manifestations of AIDS. Medicine (Baltimore) 1987 Nov;66(6):407–37. - PubMed
-
- McArthur JC, Hoover DR, Bacellar H, Miller EN, Cohen BA, Becker JT, et al. Dementia in AIDS patients: incidence and risk factors. Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. Neurology. 1993;43(11):2245–52. - PubMed
-
- Michaels J, Sharer LR, Epstein LG. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of the nervous system: a review. Immunodefic Rev. 1988;1(1):71–104. - PubMed
-
- Koenig S, Gendelman HE, Orenstein JM, Canto MCD, Pezeshkpour GH, Yungbluth M, et al. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986;233(4768):1089–93. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
