Phonophoresis and the absorption of dexamethasone in the presence of an occlusive dressing
- PMID: 18059989
- PMCID: PMC1978471
Phonophoresis and the absorption of dexamethasone in the presence of an occlusive dressing
Abstract
Context: Phonophoresis is purported to represent a method to apply topical medications through the skin to treat soft tissue injuries and inflammatory conditions. Few data are available to demonstrate the clinical effectiveness of the treatment.
Objective: To determine the effect of ultrasound on the transcutaneous absorption of dexamethasone when occluded with a dressing.
Design: Crossover design.
Setting: University general clinical research center.
Patients or other participants: Ten healthy subjects (age = 29.2 +/- 8.8 years; height = 170.0 +/- 3.9 cm; mass = 67.5 +/- 18.4 kg).
Intervention(s): Two grams of 0.33% dexamethasone cream were applied to a 10-cm (2) area on the anterior forearm. The drug was applied to the skin and occluded with a dressing for 30 minutes before the ultrasound and sham ultrasound treatments. The treatments were applied over the drug and occlusive dressing. Ultrasound treatments were delivered at an intensity of 1.0 W/cm (2) (50% pulsed) at an output frequency of 3 MHz for 5 minutes and compared with sham ultrasound treatments that were delivered at an intensity of 0.0 W/cm (2) (50% pulsed) at an output frequency of 3 MHz for 5 minutes. All subjects received both the ultrasound and sham treatments, and the order in which subjects received the treatments was counterbalanced.
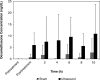
Main outcome measure(s): Serum samples were drawn before treatment and immediately posttreatment and at 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 hours posttreatment. Using high-performance liquid chromatography, we analyzed serum to determine dexamethasone concentrations.
Results: A 2-way repeated-measures analysis of variance (condition x time) revealed a significant main effect for ultrasound treatment ( P = .047). The rate of appearance and the total concentration of dexamethasone in the serum were greater in subjects after phonophoresis than after sham ultrasound. The sham group had only trace amounts of dexamethasone in the serum, indicating that drug absorption was negligible without the ultrasound energy. The effect size of the phonophoresis condition fell within a 95% confidence interval after the baseline measurement.
Conclusions: We found that a phonophoretic effect occurred with dexamethasone when its application saturated the skin.
Keywords: skin saturation; therapeutic ultrasound; ultrasound.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate Penetration During Phonophoresis at 2 Ultrasound Frequencies.J Athl Train. 2020 Jun 23;55(6):628-635. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-556-18. J Athl Train. 2020. PMID: 32320285 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phonophoretic delivery of 10% hydrocortisone through the epidermis of humans as determined by serum cortisol concentrations.Phys Ther. 1996 Jul;76(7):738-45; discussion 746-9. doi: 10.1093/ptj/76.7.738. Phys Ther. 1996. PMID: 8677278 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of phonophoresis with corticosteroids: a controlled pilot study.J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1993 Nov;18(5):590-600. doi: 10.2519/jospt.1993.18.5.590. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1993. PMID: 8268961 Clinical Trial.
-
The use of ultrasound as an enhancer for transcutaneous drug delivery: phonophoresis.Phys Ther. 1995 Jun;75(6):539-53. doi: 10.1093/ptj/75.6.539. Phys Ther. 1995. PMID: 7770499 Review.
-
Phonophoresis: efficiency, mechanisms and skin tolerance.Int J Pharm. 2002 Aug 28;243(1-2):1-15. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5173(02)00299-5. Int J Pharm. 2002. PMID: 12176291 Review.
Cited by
-
Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate Penetration During Phonophoresis at 2 Ultrasound Frequencies.J Athl Train. 2020 Jun 23;55(6):628-635. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-556-18. J Athl Train. 2020. PMID: 32320285 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy of phonophoresis on electrophysiological studies of the patients with carpal tunnel syndrome.Rheumatol Int. 2012 Oct;32(10):3235-42. doi: 10.1007/s00296-011-2171-9. Epub 2011 Oct 29. Rheumatol Int. 2012. PMID: 22038191 Clinical Trial.
-
Potential Utility of Ultrasound-Enhanced Delivery of Antibiotics, Anti-Inflammatory Agents, and Nutraceuticals: A Mini Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Sep 22;11(10):1290. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101290. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36289948 Free PMC article.
-
[The sonodynamic effects of Chlorin e6 on the proliferation of human lung adenocarcinoma cell SPCA-1].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2010 Mar;13(3):201-5. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2010.03.03. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20673516 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems and Their Use in Obesity Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 25;22(23):12754. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312754. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884558 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kleinkort JA, Wood F. Phonophoresis with 1 percent versus 10 percent hydrocortisone. Phys Ther. 1975;55:1320–1324. - PubMed
-
- Davick JP, Martin RK, Albright JP. Distribution and deposition of tritiated cortisol using phonophoresis. Phys Ther. 1988;68:1672–1675. - PubMed
-
- Stratford PW, Levy DR, Gauldie S, Miseferi D, Levy K. The evaluation of phonophoresis and friction massage as treatments for extensor carpi radialis tendinitis: a randomized controlled trial. Physiother Can. 1989;41:93–99.
-
- Byl NN, McKenzie AL, Halliday B, Wong T, O'Connell J. The effects of phonophoresis with corticosteroids: a controlled pilot study. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1993;18:590–600. - PubMed
-
- Bare AC, McAnaw MB, Pritchard AE. Phonophoretic delivery of 10% hydrocortisone through the epidermis of humans as determined by serum cortisol concentrations. Phys Ther. 1996;76:738–749. et al. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
