Mutations in the EGFR kinase domain mediate STAT3 activation via IL-6 production in human lung adenocarcinomas
- PMID: 18060032
- PMCID: PMC2096430
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI31871
Mutations in the EGFR kinase domain mediate STAT3 activation via IL-6 production in human lung adenocarcinomas
Abstract
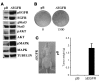
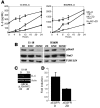
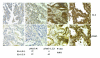
Persistently activated or tyrosine-phosphorylated STAT3 (pSTAT3) is found in 50% of lung adenocarcinomas. pSTAT3 is found in primary adenocarcinomas and cell lines harboring somatic-activating mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR. Treatment of cell lines with either an EGFR inhibitor or an src kinase inhibitor had no effect on pSTAT3 levels, whereas a pan-JAK inhibitor (P6) blocked activation of STAT3 and inhibited tumorigenesis. Cell lines expressing these persistently activated mutant EGFRs also produced high IL-6 levels, and blockade of the IL-6/gp130/JAK pathway led to a decrease in pSTAT3 levels. In addition, reduction of IL-6 levels by RNA interference led to a decrease in tumorigenesis. Introduction of persistently activated EGFR into immortalized breast epithelial cells led to tumorigenesis, IL-6 expression, and STAT3 activation, all of which could be inhibited with P6 or gp130 blockade. Furthermore, inhibition of EGFR activity in multiple cell lines partially blocked transcription of IL-6 and concurrently decreased production and release of IL-6. Finally, immunohistochemical analysis revealed a positive correlation between pSTAT3 and IL-6 positivity in primary lung adenocarcinomas. Therefore, mutant EGFR could activate the gp130/JAK/STAT3 pathway by means of IL-6 upregulation in primary human lung adenocarcinomas, making this pathway a potential target for cancer treatment.
Figures

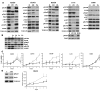
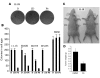
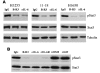
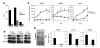

Comment in
-
IL-6 involvement in epithelial cancers.J Clin Invest. 2007 Dec;117(12):3660-3. doi: 10.1172/JCI34237. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 18060028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jett J.R., Midthun D.E. Screening for lung cancer: current status and future directions: Thomas A. Neff lecture. Chest. 2004;125:158S–162S. - PubMed
-
- Hayes D.N., et al. Gene expression profiling reveals reproducible human lung adenocarcinoma subtypes in multiple independent patient cohorts. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:5079–5090. - PubMed
-
- Lynch T.J., et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez J.G., et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Riely G.J., Politi K.A., Miller V.A., Pao W. Update on epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006;12:7232–7241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

