A genomic background based method for association analysis in related individuals
- PMID: 18060068
- PMCID: PMC2093991
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001274
A genomic background based method for association analysis in related individuals
Abstract
Background: Feasibility of genotyping of hundreds and thousands of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in thousands of study subjects have triggered the need for fast, powerful, and reliable methods for genome-wide association analysis. Here we consider a situation when study participants are genetically related (e.g. due to systematic sampling of families or because a study was performed in a genetically isolated population). Of the available methods that account for relatedness, the Measured Genotype (MG) approach is considered the 'gold standard'. However, MG is not efficient with respect to time taken for the analysis of genome-wide data. In this context we proposed a fast two-step method called Genome-wide Association using Mixed Model and Regression (GRAMMAR) for the analysis of pedigree-based quantitative traits. This method certainly overcomes the drawback of time limitation of the measured genotype (MG) approach, but pays in power. One of the major drawbacks of both MG and GRAMMAR, is that they crucially depend on the availability of complete and correct pedigree data, which is rarely available.
Methodology: In this study we first explore type 1 error and relative power of MG, GRAMMAR, and Genomic Control (GC) approaches for genetic association analysis. Secondly, we propose an extension to GRAMMAR i.e. GRAMMAR-GC. Finally, we propose application of GRAMMAR-GC using the kinship matrix estimated through genomic marker data, instead of (possibly missing and/or incorrect) genealogy.
Conclusion: Through simulations we show that MG approach maintains high power across a range of heritabilities and possible pedigree structures, and always outperforms other contemporary methods. We also show that the power of our proposed GRAMMAR-GC approaches to that of the 'gold standard' MG for all models and pedigrees studied. We show that this method is both feasible and powerful and has correct type 1 error in the context of genome-wide association analysis in related individuals.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
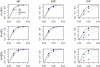
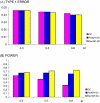
References
-
- Risch N, Merikangas K. The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science. 1996;273:1516–1517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

