Immuno-proteomic approach to excitation--contraction coupling in skeletal and cardiac muscle: molecular insights revealed by the mitsugumins
- PMID: 18061662
- PMCID: PMC3059838
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2007.10.006
Immuno-proteomic approach to excitation--contraction coupling in skeletal and cardiac muscle: molecular insights revealed by the mitsugumins
Abstract
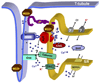
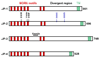
A comprehensive understanding of excitation-contraction (E-C) coupling in skeletal and cardiac muscle requires that all the major components of the Ca(2+) release machinery be resolved. We utilized a unique immuno-proteomic approach to generate a monoclonal antibody library that targets proteins localized to the skeletal muscle triad junction, which provides a structural context to allow efficient E-C coupling. Screening of this library has identified several mitsugumins (MG); proteins that can be localized to the triad junction in mammalian skeletal muscle. Many of these proteins, including MG29 and junctophilin, are important components in maintaining the structural integrity of the triad junction. Other triad proteins, such as calumin, play a more direct role in regulation of muscle Ca(2+) homeostasis. We have recently identified a family of trimeric intracellular cation-selective (TRIC) channels that allow for K(+) movement into the endoplasmic or sarcoplasmic reticulum to counter a portion of the transient negative charge produced by Ca(2+) release into the cytosol. Further study of TRIC channel function and other novel mitsugumins will increase our understanding of E-C coupling and Ca(2+) homoeostasis in muscle physiology and pathophysiology.
Figures


References
-
- Ma J, Pan Z. Junctional membrane structure and store operated calcium entry in muscle cells. Front Biosci. 2003;8:d242–d255. - PubMed
-
- Franzini-Armstrong C, Jorgensen AO. Structure and development of E–C coupling units in skeletal muscle. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1994;56:509–534. - PubMed
-
- Meissner G. Ryanodine receptor/Ca2+ release channels and their regulation by endogenous effectors. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1994;56:485–508. - PubMed
-
- Fill M, Copello JA. Ryanodine receptor calcium release channels. Physiol. Rev. 2002;82:893–922. - PubMed
-
- Farrell EF, Antaramian A, Benkusky N, Zhu X, Rueda A, Gomez AM, Valdivia HH. Regulation of cardiac excitation–contraction coupling by sorcin, a novel modulator of ryanodine receptors. Biol. Res. 2004;37:609–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

