The plasticizer butyl benzyl phthalate induces genomic changes in rat mammary gland after neonatal/prepubertal exposure
- PMID: 18062813
- PMCID: PMC2200869
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-453
The plasticizer butyl benzyl phthalate induces genomic changes in rat mammary gland after neonatal/prepubertal exposure
Abstract
Background: Phthalate esters like n-butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP) are widely used plasticizers. BBP has shown endocrine-disrupting properties, thus having a potential effect on hormone-sensitive tissues. The aim of this study is to determine the effect of neonatal/prepubertal exposure (post-natal days 2-20) to BBP on maturation parameters and on the morphology, proliferative index and genomic signature of the rat mammary gland at different ages of development (21, 35, 50 and 100 days).
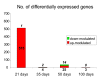
Results: Here we show that exposure to BBP increased the uterine weight/body weight ratio at 21 days and decreased the body weight at time of vaginal opening. BBP did not induce significant changes on the morphology of the mammary gland, but increased proliferative index in terminal end buds at 35 days and in lobules 1 at several ages. Moreover, BBP had an effect on the genomic profile of the mammary gland mainly at the end of the exposure (21 days), becoming less prominent thereafter. By this age a significant number of genes related to proliferation and differentiation, communication and signal transduction were up-regulated in the glands of the exposed animals.
Conclusion: These results suggest that BBP has an effect in the gene expression profile of the mammary gland.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In utero exposure to butyl benzyl phthalate induces modifications in the morphology and the gene expression profile of the mammary gland: an experimental study in rats.Environ Health. 2011 Jan 17;10(1):5. doi: 10.1186/1476-069X-10-5. Environ Health. 2011. PMID: 21241498 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of butyl benzyl phthalate exposure during pregnancy and lactation on the post-involution mammary gland.Reprod Toxicol. 2023 Dec;122:108470. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108470. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Reprod Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37743007
-
The plasticizer benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) inhibits 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA)-induced rat mammary DNA adduct formation and tumorigenesis.Carcinogenesis. 1997 Aug;18(8):1669-73. doi: 10.1093/carcin/18.8.1669. Carcinogenesis. 1997. PMID: 9276647
-
Assessment of estrogenic potential of di-n-butyl phthalate and butyl benzyl phthalate in vivo.Toxicol Ind Health. 2015 Dec;31(12):1296-303. doi: 10.1177/0748233713491803. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Toxicol Ind Health. 2015. PMID: 23833243
-
Benzyl butyl phthalate non-linearly affects rat Leydig cell development during puberty.Toxicol Lett. 2019 Oct 10;314:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.07.016. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Toxicol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31319113
Cited by
-
Removal of the endocrine disrupter butyl benzyl phthalate from the environment.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Jun;87(1):61-73. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2570-y. Epub 2010 Apr 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20396882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomics in the assessment of chemical-induced reproductive and developmental outcomes using non-invasive biological fluids: application to the study of butylbenzyl phthalate.J Appl Toxicol. 2009 Nov;29(8):703-14. doi: 10.1002/jat.1462. J Appl Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19731247 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing and Characterization of αs2-Casein Gene (CSN1S2) in the Old-World Camels Have Proven Genetic Variations Useful for the Understanding of Species Diversification.Animals (Basel). 2023 Sep 4;13(17):2805. doi: 10.3390/ani13172805. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37685069 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine disruptors and the breast: early life effects and later life disease.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2013 Mar;18(1):43-61. doi: 10.1007/s10911-013-9275-7. Epub 2013 Feb 17. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 23417729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fungal biodegradation of dibutyl phthalate and toxicity of its breakdown products on the basis of fungal and bacterial growth.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Nov;30(11):2811-9. doi: 10.1007/s11274-014-1705-1. Epub 2014 Jul 26. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25063688
References
-
- IPCS . In: Concise international chemical assessment document 17 - Butyl benzyl phthalate. WHO , editor. Geneva, Switzerland ; 1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

