Human monoclonal antibodies by immortalization of memory B cells
- PMID: 18063358
- PMCID: PMC7127177
- DOI: 10.1016/j.copbio.2007.10.011
Human monoclonal antibodies by immortalization of memory B cells
Abstract
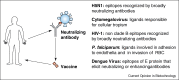
The administration of hyper immune sera to prevent or treat life-threatening infections is a remarkable milestone in medicine and biotechnology that has been achieved more than a century ago. Yet, the therapeutic use of monoclonal antibodies in this field has developed slowly over the last decades. Here we compare and contrast current methods to generate human monoclonal antibodies and highlight the advantages of exploiting the human antibody repertoire using a novel method that allows efficient immortalization and cloning of human memory B cells. This method, which has been successfully applied to isolate broadly neutralizing antibodies against SARS and H5N1 influenza viruses, is expected to accelerate the development of therapeutics in the field of infectious diseases not only by providing neutralizing antibodies for passive serotherapy, but also by generating relevant information for vaccine design.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heterosubtypic neutralizing monoclonal antibodies cross-protective against H5N1 and H1N1 recovered from human IgM+ memory B cells.PLoS One. 2008;3(12):e3942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003942. Epub 2008 Dec 16. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 19079604 Free PMC article.
-
Antigenic fingerprinting of H5N1 avian influenza using convalescent sera and monoclonal antibodies reveals potential vaccine and diagnostic targets.PLoS Med. 2009 Apr 21;6(4):e1000049. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000049. Epub 2009 Apr 21. PLoS Med. 2009. PMID: 19381279 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by a human monoclonal SARS-CoV antibody.Nature. 2020 Jul;583(7815):290-295. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2349-y. Epub 2020 May 18. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32422645
-
Human monoclonal antibodies to the S glycoprotein and related proteins as potential therapeutics for SARS.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2005 Apr;7(2):151-6. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15844623 Review.
-
Efficient Methods To Isolate Human Monoclonal Antibodies from Memory B Cells and Plasma Cells.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Oct;2(5). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.AID-0018-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 26104354 Review.
Cited by
-
Potent Neutralization Ability of a Human Monoclonal Antibody Against Serotype 1 Dengue Virus.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jun 6;9:1214. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01214. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29928270 Free PMC article.
-
Deconstructing the Antiviral Neutralizing-Antibody Response: Implications for Vaccine Development and Immunity.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Oct 26;80(4):989-1010. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00024-15. Print 2016 Dec. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27784796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression Cloning of Antibodies from Single Human B Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2865:103-124. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4188-0_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39424722
-
Antibodies, repertoires and microdevices in antibody discovery and characterization.Lab Chip. 2024 Feb 27;24(5):1207-1225. doi: 10.1039/d3lc00887h. Lab Chip. 2024. PMID: 38165819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A welcome burst of human antibodies.Nat Biotechnol. 2008 Aug;26(8):886-7. doi: 10.1038/nbt0808-886. Nat Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18688242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behring, Kitasato [On the development of immunity to diphtheria and tetanus in animals] Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1965;90:2183. - PubMed
-
- Casadevall A., Dadachova E., Pirofski L.A. Passive antibody therapy for infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:695–703. - PubMed
-
- Johnson S., Oliver C., Prince G.A., Hemming V.G., Pfarr D.S., Wang S.C., Dormitzer M., O’Grady J., Koenig S., Tamura J.K. Development of a humanized monoclonal antibody (MEDI-493) with potent in vitro and in vivo activity against respiratory syncytial virus. J Infect Dis. 1997;176:1215–1224. - PubMed
-
- Feldmann M., Maini R.N. Anti-TNF alpha therapy of rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned? Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:163–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous