Human chorionic gonadotropin stimulates trophoblast invasion through extracellularly regulated kinase and AKT signaling
- PMID: 18063683
- PMCID: PMC2974217
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2007-1282
Human chorionic gonadotropin stimulates trophoblast invasion through extracellularly regulated kinase and AKT signaling
Abstract
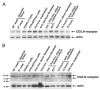
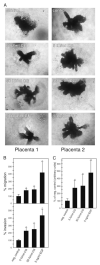
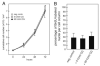
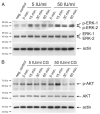
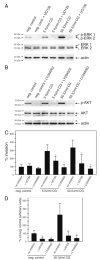
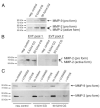
Chorionic gonadotropin (CG) is indispensable for human pregnancy because it controls implantation, decidualization, and placental development. However, its particular role in the differentiation process of invasive trophoblasts has not been fully unraveled. Here we demonstrate that the hormone promotes trophoblast invasion and migration in different trophoblast model systems. RT-PCR and Western blot analyses revealed expression of the LH/CG receptor in trophoblast cell lines and different trophoblast primary cultures. In vitro, CG increased migration and invasion of trophoblastic SGHPL-5 cells through uncoated and Matrigel-coated transwells, respectively. The hormone also increased migration of first-trimester villous explant cultures on collagen I. Proliferation of the trophoblast cell line and villous explant cultures measured by cumulative cell numbers and in situ 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine labeling, respectively, was unaffected by CG. Addition of the hormone activated ERK-1/2 and AKT in SGHPL-5 cells and pure, extravillous trophoblasts. Inhibition of MAPK kinase/ERK and phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase/AKT blocked phosphorylation of the kinases and attenuated CG-dependent invasion of SGHPL-5 cells. Similarly, the inhibitors decreased hormone-stimulated migration in villous explant cultures. Western blot analyses and gelatin zymography suggested that CG increased matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 protein levels and activity in both culture systems. Inhibition of ERK or AKT diminished CG-induced MMP-2 expression. In summary, the data demonstrate that CG promotes trophoblast invasion and migration through activation of ERK and AKT signaling involving their downstream effector MMP-2. Because the increase of CG during the first trimester of pregnancy correlates with rising trophoblast motility, the hormone could be a critical regulator of the early invasion process.
Figures


References
-
- Pierce JG, Parsons TF. Glycoprotein hormones: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:465–495. - PubMed
-
- Tulchinsky D, Hobel CJ. Plasma human chorionic gonadotropin, estrone, estradiol, estriol, progesterone, and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone in human pregnancy. 3. Early normal pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973;117:884–893. - PubMed
-
- Rao CV, Lei ZM. The past, present and future of nongonadal LH/hCG actions in reproductive biology and medicine. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007;269:2–8. - PubMed
-
- Shi QJ, Lei ZM, Rao CV, Lin J. Novel role of human chorionic gonadotropin in differentiation of human cytotrophoblasts. Endocrinology. 1993;132:1387–1395. - PubMed
-
- Han SW, Lei ZM, Rao CV. Treatment of human endometrial stromal cells with chorionic gonadotropin promotes their morphological and functional differentiation into decidua. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1999;147:7–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

