Ku recruits XLF to DNA double-strand breaks
- PMID: 18064046
- PMCID: PMC2246615
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7401137
Ku recruits XLF to DNA double-strand breaks
Abstract
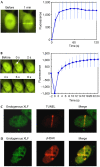
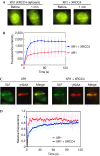
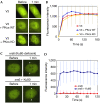
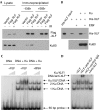
XRCC4-like factor (XLF)--also known as Cernunnos--has recently been shown to be involved in non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ), which is the main pathway for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in mammalian cells. XLF is likely to enhance NHEJ by stimulating XRCC4-ligase IV-mediated joining of DSBs. Here, we report mechanistic details of XLF recruitment to DSBs. Live cell imaging combined with laser micro-irradiation showed that XLF is an early responder to DSBs and that Ku is essential for XLF recruitment to DSBs. Biochemical analysis showed that Ku-XLF interaction occurs on DNA and that Ku stimulates XLF binding to DNA. Unexpectedly, XRCC4 is dispensable for XLF recruitment to DSBs, although photobleaching analysis showed that XRCC4 stabilizes the binding of XLF to DSBs. Our observations showed the direct involvement of XLF in the dynamic assembly of the NHEJ machinery and provide mechanistic insights into DSB recognition.
Figures
References
-
- Ahnesorg P, Smith P, Jackson SP (2006) XLF interacts with the XRCC4–DNA ligase IV complex to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Cell 124: 301–313 - PubMed
-
- Bryans M, Valenzano MC, Stamato TD (1999) Absence of DNA ligase IV protein in XR-1 cells: evidence for stabilization by XRCC4. Mutat Res 433: 53–58 - PubMed
-
- Buck D et al. (2006) Cernunnos, a novel nonhomologous end-joining factor, is mutated in human immunodeficiency with microcephaly. Cell 124: 287–299 - PubMed
-
- Callebaut I, Malivert L, Fischer A, Mornon JP, Revy P, de Villartay JP (2006) Cernunnos interacts with the XRCC4 x DNA–ligase IV complex and is homologous to the yeast nonhomologous end-joining factor Nej1. J Biol Chem 281: 13857–13860 - PubMed
-
- Calsou P, Delteil C, Frit P, Drouet J, Salles B (2003) Coordinated assembly of Ku and p460 subunits of the DNA-dependent protein kinase on DNA ends is necessary for XRCC4–ligase IV recruitment. J Mol Biol 326: 93–103 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

