Echo combination to reduce proton resonance frequency (PRF) thermometry errors from fat
- PMID: 18064715
- PMCID: PMC2780361
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.21238
Echo combination to reduce proton resonance frequency (PRF) thermometry errors from fat
Abstract
Purpose: To validate echo combination as a means to reduce errors caused by fat in temperature measurements with the proton resonance frequency (PRF) shift method.
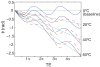
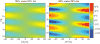
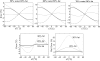
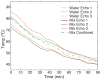
Materials and methods: Computer simulations were performed to study the behavior of temperature measurement errors introduced by fat as a function of echo time. Error reduction by combining temperature images acquired at different echo times was investigated. For experimental verification, three echoes were acquired in a refocused gradient echo acquisition. Temperature images were reconstructed with the PRF shift method for the three echoes and then combined in a weighted average. Temperature measurement errors in the combined image and the individual echoes were compared for pure water and different fractions of fat in a computer simulation and for a phantom containing a homogenous mixture with 20% fat in an MR experiment.
Results: In both simulation and MR measurement, the presence of fat caused severe temperature underestimation or overestimation in the individual echoes. The errors were substantially reduced after echo combination. Residual errors were about 0.3 degrees C for 10% fat and 1 degrees C for 20% fat.
Conclusion: Echo combination substantially reduces temperature measurement errors caused by small fractions of fat. This technique then eliminates the need for fat suppression in tissues such as the liver.
Figures
References
-
- Hindman JC. Proton resonance shift of water in gas and liquid states. Journal of Chemical Physics. 1966;44:4582–92.
-
- Woodard HQ, White DR. The composition of body-tissues. British Journal of Radiology. 1986;59:1209–1219. - PubMed
-
- Hussain H, Chenevert T, Londy F, Gulani V, Swanson S, McKenna B, Appelman H, Adusumilli S, Greenson J, Conjeevaram H. Hepatic fat fraction: MR imaging for quantitative measurement and display–early experience. Radiology. 2005;237:1048–55. - PubMed
-
- de Zwart JA, Vimeux FC, Delalande C, Canioni P, Moonen CT. Fast lipid-suppressed MR temperature mapping with echo-shifted gradient-echo imaging and spectral-spatial excitation. Magn Reson Med. 1999;42:53–9. - PubMed
-
- Weidensteiner C, Quesson B, Caire-Gana B, Kerioui N, Rullier A, Trillaud H, Moonen CT. Real-time MR temperature mapping of rabbit liver in vivo during thermal ablation. Magn Reson Med. 2003;50:322–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

