Moraxella catarrhalis synthesizes an autotransporter that is an acid phosphatase
- PMID: 18065547
- PMCID: PMC2238212
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01688-07
Moraxella catarrhalis synthesizes an autotransporter that is an acid phosphatase
Abstract
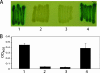
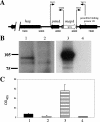
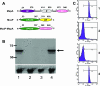
Moraxella catarrhalis O35E was shown to synthesize a 105-kDa protein that has similarity to both acid phosphatases and autotransporters. The N-terminal portion of the M. catarrhalis acid phosphatase A (MapA) was most similar (the BLAST probability score was 10(-10)) to bacterial class A nonspecific acid phosphatases. The central region of the MapA protein had similarity to passenger domains of other autotransporter proteins, whereas the C-terminal portion of MapA resembled the translocation domain of conventional autotransporters. Cloning and expression of the M. catarrhalis mapA gene in Escherichia coli confirmed the presence of acid phosphatase activity in the MapA protein. The MapA protein was shown to be localized to the outer membrane of M. catarrhalis and was not detected either in the soluble cytoplasmic fraction from disrupted M. catarrhalis cells or in the spent culture supernatant fluid from M. catarrhalis. Use of the predicted MapA translocation domain in a fusion construct with the passenger domain from another predicted M. catarrhalis autotransporter confirmed the translocation ability of this MapA domain. Inactivation of the mapA gene in M. catarrhalis strain O35E reduced the acid phosphatase activity expressed by this organism, and this mutation could be complemented in trans with the wild-type mapA gene. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the mapA gene from six M. catarrhalis strains showed that this protein was highly conserved among strains of this pathogen. Site-directed mutagenesis of a critical histidine residue (H233A) in the predicted active site of the acid phosphatase domain in MapA eliminated acid phosphatase activity in the recombinant MapA protein. This is the first description of an autotransporter protein that expresses acid phosphatase activity.
Figures
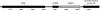





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

