Comparisons of LIPOXYGENASE3- and JASMONATE-RESISTANT4/6-silenced plants reveal that jasmonic acid and jasmonic acid-amino acid conjugates play different roles in herbivore resistance of Nicotiana attenuata
- PMID: 18065562
- PMCID: PMC2259097
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.109264
Comparisons of LIPOXYGENASE3- and JASMONATE-RESISTANT4/6-silenced plants reveal that jasmonic acid and jasmonic acid-amino acid conjugates play different roles in herbivore resistance of Nicotiana attenuata
Abstract
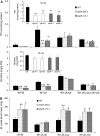
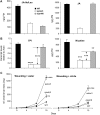
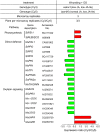
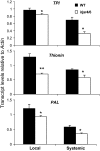
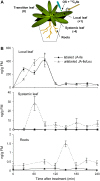
Whereas jasmonic acid (JA) and its amino acid conjugates, particularly JA-isoleucine (Ile), are known to play important roles in plant-herbivore interactions, whether other compounds also function as signals independently of JA-Ile and whether conjugates elicit systemic responses are unknown. To answer these questions, we simultaneously silenced JASMONATE-RESISTANT4 (JAR4) and JAR6, two functionally redundant enzymes in Nicotiana attenuata that conjugate JA to amino acids to produce plants (irjar4/6) with low levels of JA-Ile, JA-leucine (Leu), and JA-valine (Val; <16% of wild type). As expected, irjar4/6 plants are more vulnerable to herbivore attack, but only JA-Ile -- not JA-Leu or JA-Val -- applications restored the resistance of irjar4/6 plants, suggesting that JA-Leu and JA-Val do not mediate herbivore defense responses. Interestingly, the direct defense traits of irjar4/6 plants are significantly higher than those in LIPOXYGENASE3 (LOX3)-silenced (aslox3) plants, which are impaired in JA biosynthesis, and JA-Ile treatment could not fully restore the resistance of aslox3 plants. We thus conclude that JA, its precursors, or other metabolites complement the function of JA-Ile by eliciting a panoply of induced defenses. Similarly, transcriptional profiling of wild-type, irjar4/6, and aslox3 plants with microarrays demonstrated that JA-Ile and JA play overlapping yet distinct roles in herbivore defense. Analysis of transcripts in distal tissues demonstrated that JAR activity is essential in eliciting systemic responses. However, attempts to recover JA-(13)C(6)-Ile in systemic leaves and roots after feeding wounded leaves with (13)C(6)-Ile were unsuccessful, suggesting that JA-Ile is not a long-distance signal, but is rather synthesized after the arrival of an unknown mobile signal to systemic tissues.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Silencing threonine deaminase and JAR4 in Nicotiana attenuata impairs jasmonic acid-isoleucine-mediated defenses against Manduca sexta.Plant Cell. 2006 Nov;18(11):3303-20. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.041103. Epub 2006 Nov 3. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 17085687 Free PMC article.
-
Independently silencing two JAR family members impairs levels of trypsin proteinase inhibitors but not nicotine.Planta. 2007 Jun;226(1):159-67. doi: 10.1007/s00425-007-0477-3. Epub 2007 Feb 2. Planta. 2007. PMID: 17273867
-
RuBPCase activase (RCA) mediates growth-defense trade-offs: silencing RCA redirects jasmonic acid (JA) flux from JA-isoleucine to methyl jasmonate (MeJA) to attenuate induced defense responses in Nicotiana attenuata.New Phytol. 2014 Mar;201(4):1385-1395. doi: 10.1111/nph.12591. Epub 2013 Nov 11. New Phytol. 2014. PMID: 24491116 Free PMC article.
-
The essential role of jasmonic acid in plant-herbivore interactions--using the wild tobacco Nicotiana attenuata as a model.J Genet Genomics. 2013 Dec 20;40(12):597-606. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Nov 9. J Genet Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24377866 Review.
-
Using natural variation to achieve a whole-plant functional understanding of the responses mediated by jasmonate signaling.Plant J. 2019 Aug;99(3):414-425. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14331. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Plant J. 2019. PMID: 30927293 Review.
Cited by
-
Transporter-Mediated Subcellular Distribution in the Metabolism and Signaling of Jasmonates.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Apr 2;10:390. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00390. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31001304 Free PMC article.
-
The Active Jasmonate JA-Ile Regulates a Specific Subset of Plant Jasmonate-Mediated Resistance to Herbivores in Nature.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Jun 14;9:787. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00787. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29963064 Free PMC article.
-
Auxin Is Rapidly Induced by Herbivore Attack and Regulates a Subset of Systemic, Jasmonate-Dependent Defenses.Plant Physiol. 2016 Sep;172(1):521-32. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00940. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27485882 Free PMC article.
-
BAK1 regulates the accumulation of jasmonic acid and the levels of trypsin proteinase inhibitors in Nicotiana attenuata's responses to herbivory.J Exp Bot. 2011 Jan;62(2):641-52. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq298. Epub 2010 Oct 11. J Exp Bot. 2011. PMID: 20937731 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of systemin after herbivory is associated with increased root allocation and competitive ability in Solanum nigrum.Oecologia. 2009 Mar;159(3):473-82. doi: 10.1007/s00442-008-1230-8. Epub 2008 Nov 27. Oecologia. 2009. PMID: 19037662
References
-
- Baldwin IT, Halitschke R, Kessler A, Schittko U (2001) Merging molecular and ecological approaches in plant-insect interactions. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4 351–358 - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 57 289–300
-
- Delker C, Stenzel I, Hause B, Miersch O, Feussner I, Wasternack C (2006) Jasmonate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana—enzymes, products, regulation. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 8 297–306 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

