Apoptotic cells induce dendritic cell-mediated suppression via interferon-gamma-induced IDO
- PMID: 18067553
- PMCID: PMC2434374
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02743.x
Apoptotic cells induce dendritic cell-mediated suppression via interferon-gamma-induced IDO
Abstract
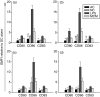
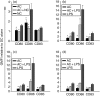
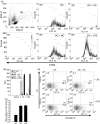
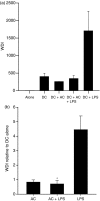
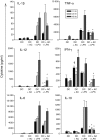
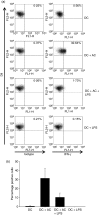
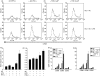
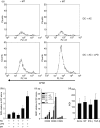
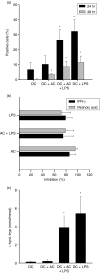
Dendritic cells (DC) are sensitive to their local environment and are affected by proximal cell death. This study investigated the modulatory effect of cell death on DC function. Monocyte-derived DC exposed to apoptotic Jurkat or primary T cells failed to induce phenotypic maturation of the DC and were unable to support CD4+ allogeneic T-cell proliferation compared with DC exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or necrotic cells. Apoptotic cells coincubated with LPS- or necrotic cell-induced mature DC significantly suppressed CD80, CD86 and CD83 and attenuated LPS-induced CD4+ T-cell proliferation. Reduced levels of interleukin-12 (IL-12), IL-10, IL-6, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) were found to be concomitant with the suppressive activity of apoptotic cells upon DC. Furthermore, intracellular staining confirmed IFN-gamma expression by DC in association with apoptotic environments. The specific generation of IFN-gamma by DC within apoptotic environments is suggestive of an anti-inflammatory role by the induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). Both neutralization of IFN-gamma and IDO blockade demonstrated a role for IFN-gamma and IDO in the suppression of CD4+ T cells. Moreover, we demonstrate that IDO expression within the DC was found to be IFN-gamma-dependent. Blocking transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) also produced a partial release in T-cell proliferation. Our study strongly suggests that apoptosis-induced DC suppression is not an immunological null event and two prime mediators underpinning these functional effects are IFN-gamma-induced IDO and TGF-beta.
Figures
References
-
- Banchereau J, Steinman RM. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 1998;392:245–52. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, Palucka AK. Dendritic cells as therapeutic vaccines against cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:296–306. - PubMed
-
- Lutz MB, Schuler G. Immature, semi-mature and fully mature dendritic cells: which signals induce tolerance or immunity? Trends Immunol. 2002;23:445–9. - PubMed
-
- Albert ML. Death-defying immunity: do apoptotic cells influence antigen processing and presentation? Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:223–31. - PubMed
-
- Fiers W, Beyaert R, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P. More than one way to die: apoptosis, necrosis and reactive oxygen damage. Oncogene. 1999;18:7719–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

