Fucoidan partly prevents CCl4-induced liver fibrosis
- PMID: 18068155
- PMCID: PMC2258315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.015
Fucoidan partly prevents CCl4-induced liver fibrosis
Abstract
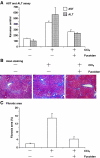
Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide extracted from brown algae, has a wide range of biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, and anti-tumor activities. In the present study, we investigated the effects of fucoidan on CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. Administration of fucoidan reduced CCl4-induced acute and chronic liver failure. Hepatic fibrosis induced by CCl4 was also attenuated by injection of fucoidan. Damage to hepatocytes and activation of hepatic stellate cells are key events in liver fibrosis, and, interestingly, treatment of hepatocytes with fucoidan prevented CCl4-induced cell death and inhibited the proliferation hepatic stellate cells. These results indicate that fucoidan might be a promising anti-fibrotic agent possessing dual functions, namely, protection of hepatocytes and inhibition of hepatic stellate cell proliferation.
Figures


References
-
- Berteau O., Mulloy B. Sulfated fucans, fresh perspectives: structures, functions, and biological properties of sulfated fucans and an overview of enzymes active toward this class of polysaccharide. Glycobiology. 2003;13:29R–40R. - PubMed
-
- Boisson-Vidal C., Haroun F., Ellouali M., Blondin C. Biological activities of polysaccharides from marine algae. Drugs Future. 1995;20:1237–1249.
-
- Canbay A., Higuchi H., Bronk S.F., Taniai M., Sebo T.J., Gores G.J. Fas enhances fibrogenesis in the bile duct ligated mouse: a link between apoptosis and fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1323–1330. - PubMed
-
- Friedman S.L. Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis. Mechanisms and treatment strategies. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993;328:1828–1835. - PubMed
-
- Friedman S.L. Evaluation of fibrosis and hepatitis C. Am. J. Med. 1999;107:27S–30S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

