Comparison of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAMe) and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) protective effects on hepatic damage when administered after acetaminophen overdose
- PMID: 18068290
- PMCID: PMC2247417
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2007.10.027
Comparison of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAMe) and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) protective effects on hepatic damage when administered after acetaminophen overdose
Abstract
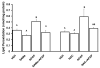
In the clinical setting, antidotes are generally administered after the occurrence of a drug overdose. Therefore, the most pertinent evaluation of any new agent should model human exposure. This study tested whether acetaminophen (APAP) hepatotoxicity was reversed when S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAMe) was administered after APAP exposure, similar to what occurs in clinical situations. Comparisons were made for potency between SAMe and N-acetylcysteine (NAC), the current treatment for APAP toxicity. Male C57BL/6 mice were fasted overnight and divided into groups: control (VEH), SAMe treated (SAMe), APAP treated (APAP), N-acetylcysteine treated (NAC), SAMe or NAC administered 1h after APAP (SAMe+APAP) and (NAC+APAP), respectively. Mice were injected intraperitoneal (i.p.) with water (VEH) or 250 mg/kg APAP (15 ml/kg). One hour later, mice were injected (i.p.) with 1.25 mmol/kg SAMe (SAMe+APAP) or NAC (NAC+APAP). Hepatotoxicity was evaluated 4h after APAP or VEH treatment. APAP induced centrilobular necrosis, increased liver weight and alanine transaminase (ALT) levels, depressed total hepatic glutathione (GSH), increased protein carbonyls and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) adducted proteins. Treatment with SAMe 1h after APAP overdose (SAMe+APAP) was hepatoprotective and was comparable to NAC+APAP. Treatment with SAMe or NAC 1h after APAP was sufficient to return total hepatic glutathione (GSH) to levels comparable to the VEH group. Western blot showed reversal of APAP mediated effects in the SAMe+APAP and NAC+APAP groups. In summary, SAMe was protective when given 1h after APAP and was comparable to NAC.
Figures





References
-
- Bajt ML, Knight TR, LeMaster JL, Jaeschke H. Acetaminophen induced oxidant stress and cell injury in cultured mouse hepatocytes: protection by N-acetyl Cysteine. Toxicol. Sci. 2004;80:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Berkeley LI, Cohen JF, Crankshaw DL, Shirota FN, Nagasawa HT. Hepatoprotection by L-cysteine-glutathione mixed disulfide, a sulfhydryl-modified prodrug of glutathione. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2003;17:95–97. - PubMed
-
- Bonfiglio MF, Traeger SM, Hulisz DT, Martin BR. Anaphylactoid reaction to intravenous acetylcysteine associated with electrocardiographic abnormalities. Ann Pharmacother. 1992;26:22–25. - PubMed
-
- Bray GP, Tredger JM, Williams R. S-Adenosylmethionine protects against APAP hepatotoxicity in two mouse models. Hepatology. 1992;15:297–301. - PubMed
-
- Bulera SJ, Cohen SD, Khairallah EA. Acetaminophen-arylated proteins are detected in hepatic subcellular fractions and numerous extra hepatic tissue in CD-1 and C57Bl/6 mice. Toxicology. 1996;109:85–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

