Cost-effectiveness analysis of laparoscopic gastric bypass, adjustable gastric banding, and nonoperative weight loss interventions
- PMID: 18069075
- PMCID: PMC2706260
- DOI: 10.1016/j.soard.2007.09.009
Cost-effectiveness analysis of laparoscopic gastric bypass, adjustable gastric banding, and nonoperative weight loss interventions
Abstract
Background: Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) and laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (LRYGB) are the two most commonly performed bariatric procedures. Although both procedures likely reduce healthcare expenditures related to the resolution of co-morbid conditions, they have different rates of perioperative risks and different rates of associated weight loss. We designed a model to evaluate the incremental cost-effectiveness of these procedures compared with nonoperative weight loss interventions and with each other.
Methods: We used a deterministic, payer-perspective model comparing the lifetime expected costs and outcomes of LAGB, LRYGB, and nonoperative treatment. The major endpoints were survival, health-related quality of life, and weight loss. Life expectancy and lifetime medical costs were calculated across age, gender, and body mass index (BMI) strata using previously published data.
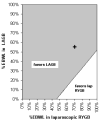
Results: For both men and women, LRYGB and LAGB were cost-effective at <$25,000/quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) even when evaluating the full range of baseline BMI and estimates of adverse outcomes, weight loss, and costs. For base-case scenarios in men (age 35 y, BMI 40 kg/m(2)), the incremental cost-effectiveness was $11,604/QALY for LAGB compared with $18,543/QALY for LRYGB. For base-case scenarios in women (age 35 y, BMI 40 kg/m(2)), the incremental cost-effectiveness was $8878/QALY for LAGB compared with $14,680/QALY for LRYGB.
Conclusion: The modeled cost-effectiveness analysis showed that both operative interventions for morbid obesity, LAGB and RYGB, were cost-effective at <$25,000 and that LAGB was more cost-effective than RYGB for all base-case scenarios.
Figures

References
-
- Mokdad A, Serdula M, Dietz W, Bowman B, Marks J, Koplan J. The continuing epidemic of obesity in the United States. JAMA. 2000;284:1650–1. - PubMed
-
- Finkelstein EA, Fiebelkorn IC, Wang G. National medical spending attributable to overweight and obesity: how much, and who’s paying? Health Aff (Millwood) 2003 Jan-Jun;Suppl:W3-219–226. - PubMed
-
- McTigue KM, Harris R, Hemphill B, et al. Screening and interventions for obesity in adults: summary of the evidence for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139:933–49. - PubMed
-
- Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292:1724–37. - PubMed
-
- Craig BM, Tseng DS. Cost-effectiveness of gastric bypass for severe obesity. Am J Med. 2002;113:491–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

