Low-dose dietary chlorophyll inhibits multi-organ carcinogenesis in the rainbow trout
- PMID: 18069110
- PMCID: PMC2404114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2007.10.034
Low-dose dietary chlorophyll inhibits multi-organ carcinogenesis in the rainbow trout
Abstract
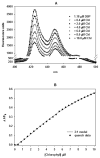
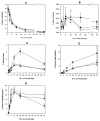
We recently reported that chlorophyll (Chl) strongly inhibits aflatoxin B(1) preneoplasia biomarkers in rats when administered by co-gavage (Simonich et al., 2007. Natural chlorophyll inhibits aflatoxin B1-induced multi-organ carcinogenesis in the rat. Carcinogenesis 28, 1294-1302.). The present study extends this by examining the effects of dietary Chl on tumor development, using rainbow trout to explore ubiquity of mechanism. Duplicate groups of 140 trout were fed diet containing 224 ppm dibenzo[a,l]pyrene (DBP) alone, or with 1000-6000 ppm Chl, for 4 weeks. DBP induced high tumor incidences in liver (51%) and stomach (56%), whereas Chl co-fed at 2000, 4000 or 6000 ppm reduced incidences in stomach (to 29%, 23% and 19%, resp., P<0.005) and liver (to 21%, 28% and 26%, resp., P<0.0005). Chlorophyllin (CHL) at 2000 ppm gave similar protection. Chl complexed with DBP in vitro (2Chl:DBP, K(d1)=4.44+/-0.46 microM, K(d2)=3.30+/-0.18 microM), as did CHL (K(d1)=1.38+/-0.32 microM, K(d2)=1.17+/-0.05 microM), possibly explaining their ability to inhibit DBP uptake into the liver by 61-63% (P<0.001). This is the first demonstration that dietary Chl can reduce tumorigenesis in any whole animal model, and that it may do so by a simple, species-independent mechanism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cancer chemoprevention by dietary chlorophylls: a 12,000-animal dose-dose matrix biomarker and tumor study.Food Chem Toxicol. 2012 Feb;50(2):341-52. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.10.065. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22079312 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The rainbow trout liver cancer model: response to environmental chemicals and studies on promotion and chemoprevention.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;155(1):121-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2011.05.013. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21704190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of dibenzo[a,l]pyrene-induced multi-organ carcinogenesis by dietary chlorophyllin in rainbow trout.Carcinogenesis. 1999 Oct;20(10):1919-26. doi: 10.1093/carcin/20.10.1919. Carcinogenesis. 1999. PMID: 10506105 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of carcinogen dose in chemoprevention studies: quantitative interrelationships between, dibenzo[a,l]pyrene dose, chlorophyllin dose, target organ DNA adduct biomarkers and final tumor outcome.Carcinogenesis. 2007 Mar;28(3):611-24. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgl174. Epub 2006 Sep 14. Carcinogenesis. 2007. PMID: 16973675
-
Chemopreventive properties of chlorophylls towards aflatoxin B1: a review of the antimutagenicity and anticarcinogenicity data in rainbow trout.Mutat Res. 1998 Mar 20;399(2):245-53. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(97)00259-5. Mutat Res. 1998. PMID: 9672663 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer chemoprevention by dietary chlorophylls: a 12,000-animal dose-dose matrix biomarker and tumor study.Food Chem Toxicol. 2012 Feb;50(2):341-52. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.10.065. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22079312 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cancer interception by interceptor molecules: mechanistic, preclinical and human translational studies with chlorophylls.Genes Environ. 2021 Mar 6;43(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s41021-021-00180-8. Genes Environ. 2021. PMID: 33676582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrospective and Prospective Look at Aflatoxin Research and Development from a Practical Standpoint.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Sep 27;16(19):3633. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16193633. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31569703 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of Kale and Lettuce Residues as Natural Adsorbents of the Carcinogen Aflatoxin B1 in a Dynamic Gastrointestinal Tract-Simulated Model.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Oct 31;13(11):771. doi: 10.3390/toxins13110771. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34822555 Free PMC article.
-
The rainbow trout liver cancer model: response to environmental chemicals and studies on promotion and chemoprevention.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;155(1):121-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2011.05.013. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21704190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blum CA, Xu M, Orner GA, Dario Diaz G, Li Q, Dashwood WM, Bailey GS, Dashwood RH. Promotion versus suppression of rat colon carcinogenesis by chlorophyllin and chlorophyll: modulation of apoptosis, cell proliferation, and beta-catenin/Tcf signaling. Mutat Res. 2003:523–524. 217–223. - PubMed
-
- Breinholt V, Arbogast D, Loveland P, Pereira C, Dashwood R, Hendricks J, Bailey G. Chlorophyllin chemoprevention in trout initiated by aflatoxin B(1) bath treatment: An evaluation of reduced bioavailability vs. target organ protective mechanisms. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1999;158:141–151. - PubMed
-
- Breinholt V, Hendricks J, Pereira C, Arbogast D, Bailey G. Dietary chlorophyllin is a potent inhibitor of aflatoxin B1 hepatocarcinogenesis in rainbow trout. Cancer Res. 1995a;55:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Breinholt V, Schimerlik M, Dashwood R, Bailey G. Mechanisms of chlorophyllin anticarcinogenesis against aflatoxin B1: complex formation with the carcinogen. Chem Res Toxicol. 1995b;8:506–514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

