The macroPARP genes Parp-9 and Parp-14 are developmentally and differentially regulated in mouse tissues
- PMID: 18069692
- PMCID: PMC7163462
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.21399
The macroPARP genes Parp-9 and Parp-14 are developmentally and differentially regulated in mouse tissues
Abstract
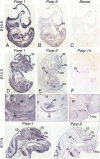
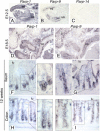
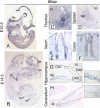
The macroPARPs Parp-9 and Parp-14 are macro domain containing poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases involved in transcriptional regulation in response to immunoregulatory cytokines. Their genes reside in the same locus (16B3), and the Parp-9 gene lies head-to-head and shares its promoter with the gene encoding its partner, Bbap. Here, we provide a detailed analysis of Parp-9, Parp-14, and Bbap expression during mouse development and adulthood. Parp-9 is developmentally regulated, and prominently expressed in the thymus and specific regions of the brain and gut. In adults, highest expression is maintained in the thymus and intestine. Parp-14 is more weakly expressed, mainly in the thymus during development and in adulthood. In addition, we show that Bbap is essentially coexpressed with Parp-9 during development and in adult mouse. However, the different levels of their transcripts detected in the developing brain and gut suggest that Bbap and Parp-9 display both common and independent tissue-specific regulations.
Figures


References
-
- Aguiar RC, Yakushijin Y, Kharbanda S, Salgia R, Fletcher JA, Shipp MA. 2000. BAL is a novel risk‐related gene in diffuse large B‐cell lymphomas that enhances cellular migration. Blood 96: 4328–4334. - PubMed
-
- Aguiar RC, Takeyama K, He C, Kreinbrink K, Shipp M. 2005. B‐aggressive lymphoma (BAL) family proteins have unique domains that modulate transcription and exhibit Poly(ADP‐ribose) polymerase activity. J Biol Chem 280: 33756–33765. - PubMed
-
- Amé JC, Spenlehauer C, de Murcia G. 2004. The PARP superfamily. Bioessays 26: 882–893. - PubMed
-
- Angelov D, Molla A, Perche PY, Hans F, Cote J, Khochbin S, Bouvet P, Dimitrov S. 2003. The histone variant macroH2A interferes with transcription factor binding and SWI/SNF nucleosome remodeling. Mol Cell 11: 1033–1041. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis‐Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. 1999. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284: 770–776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

