Telbivudine: a new treatment for chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 18069753
- PMCID: PMC4171223
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i46.6150
Telbivudine: a new treatment for chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
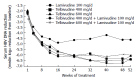
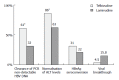
Three hundred and fifty million people worldwide are estimated to be chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. 15%-40% of these subjects will develop cirrhosis, liver failure or hepatocellular carcinoma during their life. The treatment of chronic hepatitis B has improved dramatically over the last decade merits to the advent of nucleoside/nucleotide analogues and the use of pegylated interferons. Approved drugs for chronic hepatitis B treatment include: standard interferon-alpha 2b, pegylated interferon-alpha 2a, lamivudine, adefovir dipivoxil, and entecavir. Unfortunately, these agents are not effective in all patients and are associated with distinct side effects. Interferons have numerous side effects and nucleoside or nucleotide analogues, which are well tolerated, need to be used for prolonged periods, even indefinitely. However, prolonged treatment with nucleoside or nucleotide analogues is associated with a high rate of resistance. Telbivudine is a novel, orally administered nucleoside analogue for use in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. In contrast to other nucleoside analogues, Telbivudine has not been associated with inhibition of mammalian DNA polymerase with mitochondrial toxicity. Telbivudine has demonstrated potent activity against hepatitis B with a significantly higher rate of response and superior viral suppression compared with lamivudine, the standard treatment. Telbivudine has been generally well tolerated, with a low adverse effect profile, and at its effective dose, no dose-limiting toxicity has been observed. Telbivudine is one of the most potent antiviral agents for chronic hepatitis B virus and was approved by the FDA in late 2006.
Figures
References
-
- Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1733–1745. - PubMed
-
- Mohanty SR, Kupfer SS, Khiani V. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;3:446–458. - PubMed
-
- Beasley RP. Hepatitis B virus. The major etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1988;61:1942–1956. - PubMed
-
- McMahon BJ, Holck P, Bulkow L, Snowball M. Serologic and clinical outcomes of 1536 Alaska Natives chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:759–768. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer. 2001;94:153–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources