Effect of Breathwalk on body composition, metabolic and mood state in chronic hepatitis C patients with insulin resistance syndrome
- PMID: 18069762
- PMCID: PMC4171232
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i46.6213
Effect of Breathwalk on body composition, metabolic and mood state in chronic hepatitis C patients with insulin resistance syndrome
Abstract
Aim: To identify the anthropometric, metabolic and mood state in hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected patients from the west of Mexico and to evaluate the effect of Breathwalk (BW), a combination of walking, synchronized breathing and focussed attention, on those patients.
Methods: In an experimental study, 17 patients with serological and molecular diagnosis of HCV, not receiving pharmacological treatment, were studied. One hour sessions of BW were practiced 3 times at week for six months. Body composition was assessed by electric impedance. Biochemical profiles and insulin resistance (IR) risk was assessed by conventional methods. Mood state was evaluated with specific and open questions at the beginning and at the end of the program.
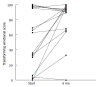
Results: Seventy percent of patients were overweight or obese, and 77% of the patients presented with IR at the beginning of the study. Improvements were observed at the 3rd mo, and statistically significant differences were recorded at the 6th mo using the fitness score (76 vs 83, P < 0.01), in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (106 +/- 93 U/L vs 59 +/- 32 U/L, P < 0.01), total bilirubin (0.09 +/- 1 mg/dL vs 0.62 +/- 0.2 mg/dL, P < 0.01), ALT/AST ratio (1.04 vs 0.70, P < 0.01), triglycerides (165 +/- 86 mg/dL vs 124 +/- 49 mg/dL, P < 0.01) and the IR risk (4.0 vs 2.7). Most patients (88%) indicated to feel better at the end of BW (P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Breathwalk has an important effect on body composition, lipid profile and liver enzymes. It is also easy, inexpensive and has a beneficial effect on metabolic and mood state in HCV patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Factors Associated with Insulin Resistance in Patients with Chronic HCV Genotype 1 Infection without Obesity or Type 2 Diabetes.J Am Coll Nutr. 2016 Jul;35(5):436-42. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2015.1072756. Epub 2016 Mar 2. J Am Coll Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26933768
-
Impact of Moderate Alcohol Discontinuation on Insulin Action and Secretion in Latinos With and Without Hepatitis C.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2018 Mar;42(3):492-499. doi: 10.1111/acer.13576. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2018. PMID: 29220547 Free PMC article.
-
Are elevated aminotransferases and decreased bilirubin additional characteristics of the metabolic syndrome?Obes Res. 1997 Mar;5(2):105-14. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1997.tb00650.x. Obes Res. 1997. PMID: 9112245
-
Associations of physical activity and fitness with hepatic steatosis, liver enzymes, and insulin resistance in children with overweight/obesity.Pediatr Diabetes. 2020 Jun;21(4):565-574. doi: 10.1111/pedi.13011. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Pediatr Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32237015 Clinical Trial.
-
Chronic hepatitis C infection is associated with insulin resistance and lipid profiles.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 May;30(5):879-84. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12313. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 23808794
Cited by
-
Genomic medicine in gastroenterology: A new approach or a new specialty?World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jul 21;21(27):8227-37. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8227. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26217074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of treadmill walking on cardiometabolic risk factors and liver function markers in older adults with MASLD: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025 Apr 25;17(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13102-025-01156-9. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40275346 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C Virus, Insulin Resistance, and Steatosis.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2016 Mar 28;4(1):66-75. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2015.00051. Epub 2016 Mar 15. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27047774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of exercise participation levels with cardiometabolic health and quality of life in individuals with hepatitis C.BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2021 Mar;8(1):e000591. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2020-000591. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33762303 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary history and physical activity and risk of advanced liver disease in veterans with chronic hepatitis C infection.Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Jun;56(6):1835-47. doi: 10.1007/s10620-010-1505-x. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21188525 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hussain SA, Ferry DR, El-Gazzaz G, Mirza DF, James ND, McMaster P, Kerr DJ. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2001;12:161–172. - PubMed
-
- Petit JM, Bour JB, Galland-Jos C, Minello A, Verges B, Guiguet M, Brun JM, Hillon P. Risk factors for diabetes mellitus and early insulin resistance in chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2001;35:279–283. - PubMed
-
- Mason AL, Lau JY, Hoang N, Qian K, Alexander GJ, Xu L, Guo L, Jacob S, Regenstein FG, Zimmerman R, et al. Association of diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology. 1999;29:328–333. - PubMed
-
- Yazicioglu G, Isitan F, Altunbas H, Suleymanlar I, Ozdogan M, Balci MK, Karayalcin U. Insulin resistance in chronic hepatitis C. Int J Clin Pract. 2004;58:1020–1022. - PubMed
-
- Koike K. Hepatitis C virus infection can present with metabolic disease by inducing insulin resistance. Intervirology. 2006;49:51–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources