A novel inhibitory mechanism of mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis by a herpesviral protein
- PMID: 18069888
- PMCID: PMC2134948
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030174
A novel inhibitory mechanism of mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis by a herpesviral protein
Abstract
Upon viral infection, cells undergo apoptosis as a defense against viral replication. Viruses, in turn, have evolved elaborate mechanisms to subvert apoptotic processes. Here, we report that a novel viral mitochondrial anti-apoptotic protein (vMAP) of murine gamma-herpesvirus 68 (gammaHV-68) interacts with Bcl-2 and voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1) in a genetically separable manner. The N-terminal region of vMAP interacted with Bcl-2, and this interaction markedly increased not only Bcl-2 recruitment to mitochondria but also its avidity for BH3-only pro-apoptotic proteins, thereby suppressing Bax mitochondrial translocation and activation. In addition, the central and C-terminal hydrophobic regions of vMAP interacted with VDAC1. Consequently, these interactions resulted in the effective inhibition of cytochrome c release, leading to the comprehensive inhibition of mitochondrion-mediated apoptosis. Finally, vMAP gene was required for efficient gammaHV-68 lytic replication in normal cells, but not in mitochondrial apoptosis-deficient cells. These results demonstrate that gammaHV-68 vMAP independently targets two important regulators of mitochondrial apoptosis-mediated intracellular innate immunity, allowing efficient viral lytic replication.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

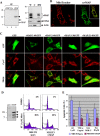


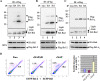
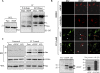
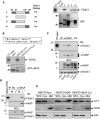

References
-
- Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE, et al. Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature. 1999;397:441–446. - PubMed
-
- Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, et al. Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 1997;91:479–489. - PubMed
-
- Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 2000;102:33–42. - PubMed
-
- Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Silke J, Connolly LM, et al. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell. 2000;102:43–53. - PubMed
-
- Kuwana T, Mackey MR, Perkins G, Ellisman MH, Latterich M, et al. Bid, Bax, and lipids cooperate to form supramolecular openings in the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cell. 2002;111:331–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

