Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA miR-BART2 down-regulates the viral DNA polymerase BALF5
- PMID: 18073197
- PMCID: PMC2241876
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm1080
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA miR-BART2 down-regulates the viral DNA polymerase BALF5
Abstract
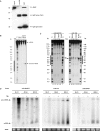
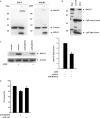
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been implicated in sequence-specific cleavage, translational repression or deadenylation of specific target mRNAs resulting in post-transcriptional gene silencing. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) encodes 23 miRNAs of unknown function. Here we show that the EBV-encoded miRNA miR-BART2 down-regulates the viral DNA polymerase BALF5. MiR-BART2 guides cleavage within the 3'-untranslated region (3'UTR) of BALF5 by virtue of its complete complementarity to its target. Induction of the lytic viral replication cycle results in a reduction of the level of miR-BART2 with a strong concomitant decrease of cleavage of the BALF5 3'UTR. Expression of miR-BART2 down-regulates the activity of a luciferase reporter gene containing the BALF5 3'UTR. Forced expression of miR-BART2 during lytic replication resulted in a 40-50% reduction of the level of BALF5 protein and a 20% reduction of the amount of virus released from EBV-infected cells. Our results are compatible with the notion that EBV-miR-BART2 inhibits transition from latent to lytic viral replication.
Figures



References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Filipowicz W. Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: how many mechanisms? Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17:118–126. Epub 2007 Jan 2002. - PubMed
-
- Borchert GM, Lanier W, Davidson BL. RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006;12:12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

