miR-122 targeting with LNA/2'-O-methyl oligonucleotide mixmers, peptide nucleic acids (PNA), and PNA-peptide conjugates
- PMID: 18073344
- PMCID: PMC2212241
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.844108
miR-122 targeting with LNA/2'-O-methyl oligonucleotide mixmers, peptide nucleic acids (PNA), and PNA-peptide conjugates
Abstract
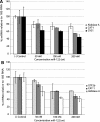
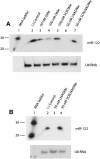
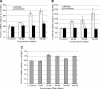
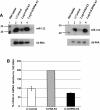
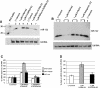
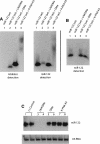
MicroRNAs are small noncoding RNAs that regulate many cellular processes in a post-transcriptional mode. MicroRNA knockdown by antisense oligonucleotides is a useful strategy to explore microRNA functionality and as potential therapeutics. MicroRNA-122 (miR-122) is a liver-specific microRNA, the main function of which has been linked with lipid metabolism and liver homeostasis. Here, we show that lipofection of an antisense oligonucleotide based on a Locked Nucleic Acids (LNA)/2'-O-methyl mixmer or electroporation of a Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA) oligomer is effective at blocking miR-122 activity in human and rat liver cells. These oligonucleotide analogs, evaluated for the first time in microRNA inhibition, are more effective than standard 2'-O-methyl oligonucleotides in binding and inhibiting microRNA action. We also show that microRNA inhibition can be achieved without the need for transfection or electroporation of the human or rat cell lines, by conjugation of an antisense PNA to the cell-penetrating peptide R6-Penetratin, or merely by linkage to just four Lys residues, highlighting the potential of PNA for future therapeutic applications as well as for studying microRNA function.
Figures
References
-
- Abes, S., Williams, D., Prevot, P., Thierry, A.R., Gait, M.J., Lebleu, B. Endosome trapping limits the efficiency of splicing correction by PNA–oligolysine conjugates. J. Control. Release. 2006;110:595–604. - PubMed
-
- Ahn, D.-G., Kourakis, M.J., Rohde, L.A., Silver, L.M., Ho, R.K. T-box gene tbx5 is essential for formation of the pectoral limb bud. Nature. 2002;417:754–758. - PubMed
-
- Albertshofer, K., Siwkowski, A.M., Wancewicz, E.V., Esau, C.C., Watanabe, T., Nishihara, K.C., Kinberger, G.A., Malik, L., Eldrup, A.B., Manoharan, M., et al. Structure–activity relationship study on a simple cationic peptide motif for cellular delivery of antisense peptide nucleic acid. J. Med. Chem. 2005;48:6741–6749. - PubMed
-
- Arzumanov, A., Walsh, A.P., Rajwanshi, V.K., Kumar, R., Wengel, J., Gait, M.J. Inhibition of HIV-1 Tat-dependent trans-activation by steric block chimeric 2′-O-methyl/LNA oligoribonucleotides. Biochemistry. 2001;40:14645–14654. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
