Diverse roles of hnRNP L in mammalian mRNA processing: a combined microarray and RNAi analysis
- PMID: 18073345
- PMCID: PMC2212255
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.725208
Diverse roles of hnRNP L in mammalian mRNA processing: a combined microarray and RNAi analysis
Abstract
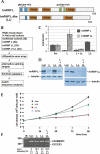
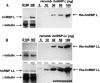
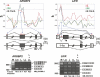
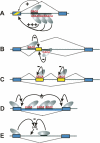
Alternative mRNA splicing patterns are determined by the combinatorial control of regulator proteins and their target RNA sequences. We have recently characterized human hnRNP L as a global regulator of alternative splicing, binding to diverse C/A-rich elements. To systematically identify hnRNP L target genes on a genome-wide level, we have combined splice-sensitive microarray analysis and an RNAi-knockdown approach. As a result, we describe 11 target genes of hnRNP L that were validated by RT-PCR and that represent several new modes of hnRNP L-dependent splicing regulation, involving both activator and repressor functions: first, intron retention; second, inclusion or skipping of cassette-type exons; third, suppression of multiple exons; and fourth, alternative poly(A) site selection. In sum, this approach revealed a surprising diversity of splicing-regulatory processes as well as poly(A) site selection in which hnRNP L is involved.
Figures




References
-
- Ast, G. How did alternative splicing evolve? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004;5:773–782. - PubMed
-
- Bilbao, D., Valcarcel, J. Getting to the heart of a splicing enhancer. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003;10:6–7. - PubMed
-
- Black, D.L. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003;72:291–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
