Influence of amineptine on changes of blood pressure evoked by norepinephrine and dopamine
- PMID: 1807368
- PMCID: PMC4532118
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1991.6.2.69
Influence of amineptine on changes of blood pressure evoked by norepinephrine and dopamine
Abstract
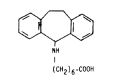
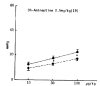
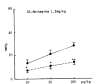
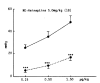
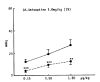
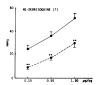
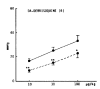
The influence of amineptine, an antidepressant currently employed having mainly selective dopaminergic neurochemical activity, on the pressor responses evoked by norepinephrine (NE) and dopamine (DA) was studied in anesthetized whole rats. Amineptine at doses of 0.5, 1.5, and 5.0 mg/kg/30 min infused into the femoral vein of the rat caused a dose-related inhibition of the pressor responses of NE and DA. The hypertensive responses of NE and DA augmented by pretreatment with reserpine, a catecholamine depletor, were also clearly depressed following the infusion of amineptine with a rate of 1.5 mg/kg/30 min. Furthermore, the pressor responses of NE and DA potentiated by pretreatment with debrisoquin, a sympathetic neuron blocker, were markedly diminished after pretreatment with the infusion of amineptine at the above same rate (1.5 mg/kg/30 min). These experimental results demonstrate that amineptine causes an inhibitory effect on the pressor responses evoked by NE and DA. It is thought that the amineptine effect may be due to the blockade of the peripheral adrenergic alpha-receptors in addition to the previously described uptake inhibition of dopamine.
Figures






References
-
- Malen CE, Poignant JC. 7-aminoheptanoic acid derivatives and potential neuropharmacological agents. 1. Experientia. 1972;28:811–812. - PubMed
-
- Offermeir J, Potgieter B, Du Preez HG, Mering PJ. Studies on the pharmacology of a new antidepressant, S1694. S Afr Med J. 1977;51:62–66. - PubMed
-
- Saminin R, Jori A, Bernasconi S, Morpugo E, Garattini S. Biochemical and pharmacological studies on amineptine (S1964) and (+) amphetamine in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978;29:555–558. - PubMed
-
- Dankova J, Boucher R, Poirier LJ. Effects of S1694 and other dopaminergic agents on circling behavior. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977;42:113–121. - PubMed
-
- Poignant JC, Avril A. Pharmacological studies on drugs acting on the social behavior of the squirrel monkey. Effects of amineptine, piribedil, d-amphetamine and amitriptyline. Arzneim-Forsch. 1979;28:267–271. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
