From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain
- PMID: 18073775
- PMCID: PMC2919277
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn2297
From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain
Abstract
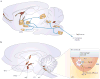
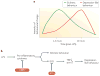
In response to a peripheral infection, innate immune cells produce pro-inflammatory cytokines that act on the brain to cause sickness behaviour. When activation of the peripheral immune system continues unabated, such as during systemic infections, cancer or autoimmune diseases, the ensuing immune signalling to the brain can lead to an exacerbation of sickness and the development of symptoms of depression in vulnerable individuals. These phenomena might account for the increased prevalence of clinical depression in physically ill people. Inflammation is therefore an important biological event that might increase the risk of major depressive episodes, much like the more traditional psychosocial factors.
Figures


References
-
- Hart BL. Biological basis of the behavior of sick animals. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1988;12:123–137. The original description of sickness behaviour, its relationship with fever and adaptive value. - PubMed
-
- Dantzer R, Kelley KW. Stress and immunity: an integrated view of relationships between the brain and the immune system. Life Sci. 1989;44:1995–2008. - PubMed
-
- Dantzer R. Cytokine-induced sickness behavior: where do we stand? Brain Behav Immun. 2001;15:7–24. - PubMed
-
- Steptoe A. Depression and Physical Illness. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MH 069148/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 079829/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG029573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH051569/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK 064862/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK064862/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG 029573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA 024443/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH071349/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA024443/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH079829/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AG 0616710/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH069148/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023580/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG 023580/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 51569/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 71349/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

