Zinc(II) coordination complexes as membrane-active fluorescent probes and antibiotics
- PMID: 18076009
- PMCID: PMC2849105
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.200700489
Zinc(II) coordination complexes as membrane-active fluorescent probes and antibiotics
Abstract
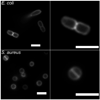
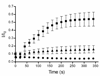
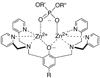
Molecular probes with zinc(II)-(2,2'-dipicolylamine) coordination complexes associate with oxyanions in aqueous solution and target biomembranes that contain anionic phospholipids. This study examines a new series of coordination complexes with 2,6-bis(zinc(II)-dipicolylamine)phenoxide as the molecular recognition unit. Two lipophilic analogues are observed to partition into the membranes of zwitterionic and anionic vesicles and induce the transport of phospholipids and hydrophilic anions (carboxyfluorescein). These lipophilic zinc complexes are moderately toxic to mammalian cells. A more hydrophilic analogue does not exhibit mammalian cell toxicity (LD(50) >50 microg mL(-1)), but it is highly active against the Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus (MIC of 1 microg mL(-1)). Furthermore, it is active against clinically important S. aureus strains that are resistant to various antibiotics, including vancomycin and oxacillin. The antibiotic action is attributed to its ability to depolarize the bacterial cell membrane. The intense bacterial staining that was exhibited by a fluorescent conjugate suggests that this family of zinc coordination complexes can be used as molecular probes for the detection and imaging of bacteria.
Figures
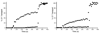




References
-
- Choi S-K. Synthetic Multivalent Molecules, Concepts and Biomedical Applications. Hoboken: Wiley; 2004.
-
- Howard GC, Kaser MR, editors. Making and Using Antibodies: A Practical Handbook. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2006.
- Mather SJ. Mol. Biosyst. 2007;3:30–35. - PubMed
-
- Dübel S, editor. Handbook of Therapeutic Antibodies. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH; 2007.
-
- Tew GN, Clements D, Tang H, Arnt H, Scott RW. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1758:1387–1392. - PubMed
- Epand RF, Schmitt MA, Gellman SH, Epand RM. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1758:1343–1350. - PubMed
- Rausch JM, Marks JR, Wimley WC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:10511–10515. - PMC - PubMed
- Odds FC, Brown AJP, Gow NAR. Trends Microbiol. 2003;11:272–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

