A real-time QCM-D approach to monitoring mammalian DNA damage using DNA adsorbed to a polyelectrolyte surface
- PMID: 18076139
- PMCID: PMC2582042
- DOI: 10.1021/bm701062f
A real-time QCM-D approach to monitoring mammalian DNA damage using DNA adsorbed to a polyelectrolyte surface
Abstract
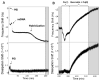
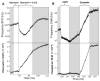
We have successfully demonstrated that the quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) can be used to monitor real-time damage to genomic mammalian DNA adsorbed to a polyelectrolyte surface. To reveal the capabilities of this technique, we exposed DNA surfaces to quercetin, an agent that has been implicated in causing DNA strand breaks in a Cu(II)-dependent fashion in vitro. We show that the QCM-D frequency and dissipation patterns that result from exposure of the DNA surfaces to quercetin-Cu(II) are consistent with the induction of DNA strand scission. We use QCM-D to furthermore demonstrate that this process is dependent on Cu(II) and that the DNA damage induced by quercetin can still be detected if Cu(II) is in situ with the DNA surface and not in solution phase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigation of double stranded DNA damage induced by quercetin-copper(II) using piezoelectric quartz crystal impedance technique and potentiometric stripping analysis.Biophys Chem. 2004 Dec 1;112(1):69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2004.07.004. Biophys Chem. 2004. PMID: 15501577
-
Quartz crystal microbalance-with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) for real time measurements of blood coagulation density and immune complement activation on artificial surfaces.Biosens Bioelectron. 2005 Jul 15;21(1):79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2004.09.026. Epub 2004 Nov 11. Biosens Bioelectron. 2005. PMID: 15967354
-
Broadband 120 MHz Impedance Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) with Calibrated Resistance and Quantitative Dissipation for Biosensing Measurements at Higher Harmonic Frequencies.Biosensors (Basel). 2016 May 25;6(2):23. doi: 10.3390/bios6020023. Biosensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27231946 Free PMC article.
-
QCM-D study of nanoparticle interactions.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2016 Jul;233:94-114. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2015.10.004. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2016. PMID: 26546115 Review.
-
Probing the Interaction between Nanoparticles and Lipid Membranes by Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring.Front Chem. 2016 Dec 5;4:46. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2016.00046. eCollection 2016. Front Chem. 2016. PMID: 27995125 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oliveira-Brett AM, Diculescu VC. Bioelectrochem. 2004;64:133–141. - PubMed
-
- Oliveira-Brett AM, Diculescu VC. Bioelectrochem. 2004;64:143–150. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Deng K, Li J, Liu S, Yao S. Biophys Chem. 2004;112:69–76. - PubMed
-
- Sahu SC, Gray GC. Cancer Lett. 1996;104:193–196. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita N, Tanemura H, Kawanishi S. Mut Res. 1999;425:107–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

