Mapping meiotic single-strand DNA reveals a new landscape of DNA double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 18076285
- PMCID: PMC2121111
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050324
Mapping meiotic single-strand DNA reveals a new landscape of DNA double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Erratum in
- PLoS Biol. 2008 Apr 29;6(4). doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060104 doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060104
Abstract
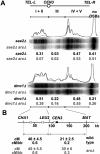
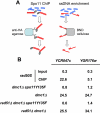
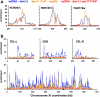
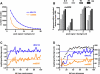
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), which are formed by the Spo11 protein, initiate meiotic recombination. Previous DSB-mapping studies have used rad50S or sae2Delta mutants, which are defective in break processing, to accumulate Spo11-linked DSBs, and report large (> or = 50 kb) "DSB-hot" regions that are separated by "DSB-cold" domains of similar size. Substantial recombination occurs in some DSB-cold regions, suggesting that DSB patterns are not normal in rad50S or sae2Delta mutants. We therefore developed a novel method to map genome-wide, single-strand DNA (ssDNA)-associated DSBs that accumulate in processing-capable, repair-defective dmc1Delta and dmc1Delta rad51Delta mutants. DSBs were observed at known hot spots, but also in most previously identified "DSB-cold" regions, including near centromeres and telomeres. Although approximately 40% of the genome is DSB-cold in rad50S mutants, analysis of meiotic ssDNA from dmc1Delta shows that most of these regions have substantial DSB activity. Southern blot assays of DSBs in selected regions in dmc1Delta, rad50S, and wild-type cells confirm these findings. Thus, DSBs are distributed much more uniformly than was previously believed. Comparisons of DSB signals in dmc1, dmc1 rad51, and dmc1 spo11 mutant strains identify Dmc1 as a critical strand-exchange activity genome-wide, and confirm previous conclusions that Spo11-induced lesions initiate all meiotic recombination.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Gerton JL, Hawley RS. Homologous chromosome interactions in meiosis: diversity amidst conservation. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:477–487. - PubMed
-
- Koehler KE, Hawley RS, Sherman S, Hassold T. Recombination and nondisjunction in humans and flies. Hum Mol Genet. 1996;5:1495–1504. - PubMed
-
- Keeney S. Mechanism and control of meiotic recombination initiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2001;52:1–53. - PubMed
-
- Bergerat A, de Massy B, Gadelle D, Varoutas PC, Nicolas A, et al. An atypical topoisomerase II from Archaea with implications for meiotic recombination. Nature. 1997;386:414–417. - PubMed
-
- Keeney S, Giroux CN, Kleckner N. Meiosis-specific DNA double-strand breaks are catalyzed by Spo11, a member of a widely conserved protein family. Cell. 1997;88:375–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

