DNA transposons and the evolution of eukaryotic genomes
- PMID: 18076328
- PMCID: PMC2167627
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.genet.40.110405.090448
DNA transposons and the evolution of eukaryotic genomes
Abstract
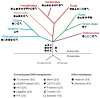
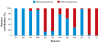
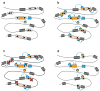
Transposable elements are mobile genetic units that exhibit broad diversity in their structure and transposition mechanisms. Transposable elements occupy a large fraction of many eukaryotic genomes and their movement and accumulation represent a major force shaping the genes and genomes of almost all organisms. This review focuses on DNA-mediated or class 2 transposons and emphasizes how this class of elements is distinguished from other types of mobile elements in terms of their structure, amplification dynamics, and genomic effect. We provide an up-to-date outlook on the diversity and taxonomic distribution of all major types of DNA transposons in eukaryotes, including Helitrons and Mavericks. We discuss some of the evolutionary forces that influence their maintenance and diversification in various genomic environments. Finally, we highlight how the distinctive biological features of DNA transposons have contributed to shape genome architecture and led to the emergence of genetic innovations in different eukaryotic lineages.
Figures
References
-
- Abrusan G, Krambeck HJ. Competition may determine the diversity of transposable elements. Theor Popul Biol. 2006;70:364–75. - PubMed
-
- Adams KL, Wendel JF. Novel patterns of gene expression in polyploid plants. Trends Genet. 2005;21:539–43. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal A, Eastman QM, Schatz DG. Transposition mediated by RAG1 and RAG2 and its implications for the evolution of the immune system. Nature. 1998;394:744–51. - PubMed
-
- Bakre AA, Rawal K, Ramaswamy R, Bhattacharya A, Bhattacharya S. The LINEs and SINEs of Entamoeba histolytica: comparative analysis and genomic distribution. Exp Parasitol. 2005;110:207–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

