Male urine signals social rank in the Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus)
- PMID: 18076759
- PMCID: PMC2222621
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7007-5-54
Male urine signals social rank in the Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus)
Abstract
Background: The urine of freshwater fish species investigated so far acts as a vehicle for reproductive pheromones affecting the behaviour and physiology of the opposite sex. However, the role of urinary pheromones in intra-sexual competition has received less attention. This is particularly relevant in lek-breeding species, such as the Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus), where males establish dominance hierarchies and there is the possibility for chemical communication in the modulation of aggression among males. To investigate whether males use urine during aggressive interactions, we measured urination frequency of dye-injected males during paired interactions between size-matched males. Furthermore, we assessed urinary volume stored in the bladder of males in a stable social hierarchy and the olfactory potency of their urine by recording of the electro-olfactogram.
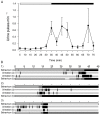
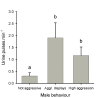
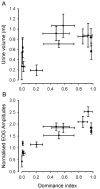
Results: Males released urine in pulses of short duration (about one second) and markedly increased urination frequency during aggressive behaviour, but did not release urine whilst submissive. In the stable hierarchy, subordinate males stored less urine than males of higher social rank; the olfactory potency of the urine was positively correlated with the rank of the male donor.
Conclusion: Dominant males store urine and use it as a vehicle for odorants actively released during aggressive disputes. The olfactory potency of the urine is positively correlated with the social status of the male. We suggest that males actively advertise their dominant status through urinary odorants which may act as a 'dominance' pheromone to modulate aggression in rivals, thereby contributing to social stability within the lek.
Figures

References
-
- Wisenden BD, Stacey NE. Fish semiochemicals and the evolution of communication networks. In: McGregor PK, editor. Animal Communication Networks. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2005. pp. 540–567.
-
- Stacey N, Sorensen P. Reproductive pheromones. In: Sloman KA, Wilson RW, Balshine S, editor. Behaviour and Physiology of Fish. London: Academic Press; 2006. pp. 359–412.
-
- Kobayashi M, Sorensen PW, Stacey NE. Hormonal and pheromonal control of spawning behavior in the goldfish. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2002;26:71–84. doi: 10.1023/A:1023375931734. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

