A novel subset of memory B cells is enriched in autoreactivity and correlates with adverse outcomes in SLE
- PMID: 18077220
- PMCID: PMC2812414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2007.10.004
A novel subset of memory B cells is enriched in autoreactivity and correlates with adverse outcomes in SLE
Abstract
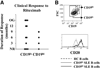
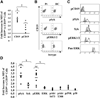
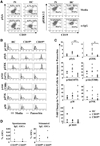
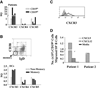
We previously reported that some systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients have a population of circulating memory B cells with >2-fold higher levels of CD19. We show here that the presence of CD19(hi) B cells correlates with long-term adverse outcomes. These B cells do not appear anergic, as they exhibit high basal levels of phosphorylated Syk and ERK1/2, signal transduce in response to BCR crosslinking, and can become plasma cells (PCs) in vitro. Autoreactive anti-Smith (Sm) B cells are enriched in this population and the degree of enrichment correlates with the log of the serum anti-Sm titer, arguing that they undergo clonal expansion before PC differentiation. PC differentiation may occur at sites of inflammation, as CD19(hi) B cells have elevated CXCR3 levels and chemotax in response to its ligand CXCL9. Thus, CD19(hi) B cells are precursors to anti-self PCs, and identify an SLE patient subset likely to experience poor clinical outcomes.
Figures


References
-
- Hahn BH. Antibodies to DNA. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1359–1368. - PubMed
-
- Su W, Madaio MP. Recent advances in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis: autoantibodies and B cells. Semin Nephrol. 2003;23:564–568. - PubMed
-
- Harris DP, Haynes L, Sayles PC, Duso DK, Eaton SM, Lepak NM, Johnson LL, Swain SL, Lund FE. Reciprocal regulation of polarized cytokine production by effector B and T cells. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:475–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

