Molecular and phenotypic data supporting distinct species statuses for Scedosporium apiospermum and Pseudallescheria boydii and the proposed new species Scedosporium dehoogii
- PMID: 18077629
- PMCID: PMC2238108
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01122-07
Molecular and phenotypic data supporting distinct species statuses for Scedosporium apiospermum and Pseudallescheria boydii and the proposed new species Scedosporium dehoogii
Abstract
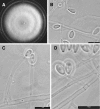
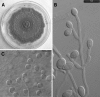
Based on the morphological, physiologic, and molecular (beta-tubulin gene) study of 141 isolates of the Pseudallescheria boydii species complex (including several synonyms) and relatives, the new species Scedosporium dehoogii is proposed. Scedosporium apiospermum and P. boydii are considered two different species and the new name Scedosporium boydii is proposed for the anamorph of the latter species. A summary of the key morphological and physiological features for distinguishing the species of Pseudallescheria/Scedosporium is provided.
Figures

References
-
- Bard, C. B., J. L. Carter, S. P. Keely, L. Huang, N. J. Pieniazek, I. N. Moura, J. M. Roberts, A. W. Hightower, M. S. Bens, A. R. Freeman, S. Lee, J. R. Stringer, J. S. Duchin, C. del Rio, D. Rimland, R. P. Baughman, D. A. Levy, V. J. Dietz, P. Simon, and T. R. Navin. 2000. Genetic variation in Pneumocystis carinii isolates from different geographic regions: implications for transmission. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 6265-272. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hughes, S. J. 1958. Revisiones hyphomycetum aliquot cum appendice de nominibus rejiciendis. Can. J. Bot. 36727-836.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

