Discrimination of herpes simplex virus type 2 strains by nucleotide sequence variations
- PMID: 18077652
- PMCID: PMC2238078
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01615-07
Discrimination of herpes simplex virus type 2 strains by nucleotide sequence variations
Abstract
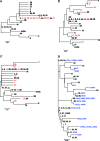
We determined the polymorphous 400-bp regions in UL53, US1, and US4 for the discrimination of herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) strains. Thirty-six HSV-2 clinical strains could be differentiated into 35 groups using these three regions and into 36 groups by additional analysis of three noncoding regions previously reported as polymorphous.
Figures

References
-
- Barrett-Muir, W., F. T. Scott, P. Aaby, J. John, P. Matondo, Q. L. Chaudhry, M. Siqueira, A. Poulsen, K. Yamanishi, and J. Breuer. 2003. Genetic variation of varicella-zoster virus: evidence for geographical separation of strains. J. Med. Virol. 70(Suppl. 1)S42-S47. - PubMed
-
- Chiba, A., T. Suzutani, M. Saijo, S. Koyano, and M. Azuma. 1998. Analysis of nucleotide sequence variations in herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, and varicella-zoster virus. Acta Virol. 42401-407. - PubMed
-
- Hammerberg, O., J. Watts, M. Chernesky, I. Luchsinger, and W. Rawls. 1983. An outbreak of herpes simplex virus type 1 in an intensive care nursery. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2290-294. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

