Tonic endovanilloid facilitation of glutamate release in brainstem descending antinociceptive pathways
- PMID: 18077685
- PMCID: PMC6673635
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3258-07.2007
Tonic endovanilloid facilitation of glutamate release in brainstem descending antinociceptive pathways
Abstract
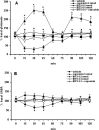
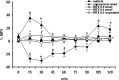
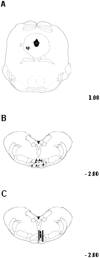
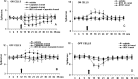
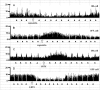
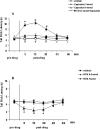
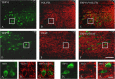
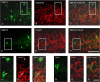
Activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) channels in the periaqueductal gray (PAG) activates OFF antinociceptive neurons of the rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM). We examined in rats the effect of intra-ventrolateral (VL)-PAG injections of TRPV1 agonists and antagonists on the nocifensive response to heat in the plantar test, neurotransmitter (glutamate and GABA) release in the RVM, and spontaneous and tail flick-related activities of RVM neurons. The localization of TRPV1 in VL-PAG and RVM neurons was examined using various markers of glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons. Intra-VL-PAG injection of capsaicin increased the threshold of thermal pain sensitivity, whereas the selective TRPV1 antagonist 5'-iodo-resiniferatoxin (I-RTX) facilitated nociceptive responses, and blocked capsaicin analgesic effect at a dose inactive per se. Intra-VL PAG capsaicin evoked a robust release of glutamate in RVM microdialysates. I-RTX, at a dose inactive per se, blocked the effect of capsaicin, and inhibited glutamate release at a higher dose. Antinociception and hyperalgesia induced by capsaicin and I-RTX, respectively, correlated with enhanced or reduced activity of RVM OFF cells. Immunohistochemical analyses suggested that several TRPV1-immunoreactive (ir) neurons in both the VL-PAG and RVM are glutamatergic and surrounded by glutamatergic and GABAergic terminals. Our data suggest that VL-PAG neurons respond to TRPV1 stimulation by releasing glutamate into the RVM, thereby activating OFF cells and producing analgesia. The results obtained with the TRPV1 antagonist alone suggest that this pathway is tonically activated by endovanilloids.
Figures
References
-
- Azkue JJ, Mateos JM, Elezgarai I, Benitez R, Lazaro E, Streit P, Grandes P. Glutamate-like immunoreactivity in ascending spinofugal afferents to the rat periaqueductal grey. Brain Res. 1998;790:74–81. - PubMed
-
- Basbaum AI, Fields HL. Endogenous pain control systems: brainstem spinal pathways and endorphin circuitry. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1984;7:309–338. - PubMed
-
- Behbehani MM. Functional characteristics of the midbrain periaqueductal gray. Prog Neurobiol. 1995;46:575–605. - PubMed
-
- Behbehani MM, Fields HL. Evidence that an excitatory connection between the periaqueductal gray and nucleus raphe magnus mediates stimulation produced analgesia. Brain Res. 1979;170:85–93. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
