Chronic CD4+ T-cell activation and depletion in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection: type I interferon-mediated disruption of T-cell dynamics
- PMID: 18077723
- PMCID: PMC2258719
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02228-07
Chronic CD4+ T-cell activation and depletion in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection: type I interferon-mediated disruption of T-cell dynamics
Abstract
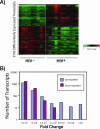
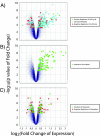
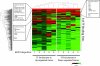
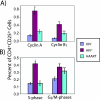
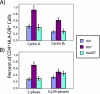
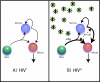
The mechanism of CD4(+) T-cell depletion during chronic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection remains unknown. Many studies suggest a significant role for chronic CD4(+) T-cell activation. We assumed that the pathogenic process of excessive CD4(+) T-cell activation would be reflected in the transcriptional profiles of activated CD4(+) T cells. Here we demonstrate that the transcriptional programs of in vivo-activated CD4(+) T cells from untreated HIV-positive (HIV(+)) individuals are clearly different from those of activated CD4(+) T cells from HIV-negative (HIV(-)) individuals. We observed a dramatic up-regulation of cell cycle-associated and interferon-stimulated transcripts in activated CD4(+) T cells of untreated HIV(+) individuals. Furthermore, we find an enrichment of proliferative and type I interferon-responsive transcription factor binding sites in the promoters of genes that are differentially expressed in activated CD4(+) T cells of untreated HIV(+) individuals compared to those of HIV(-) individuals. We confirm these findings by examination of in vivo-activated CD4(+) T cells. Taken together, these results suggest that activated CD4(+) T cells from untreated HIV(+) individuals are in a hyperproliferative state that is modulated by type I interferons. From these results, we propose a new model for CD4(+) T-cell depletion during chronic HIV-1 infection.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson, R. W., M. S. Ascher, and H. W. Sheppard. 1998. Direct HIV cytopathicity cannot account for CD4 decline in AIDS in the presence of homeostasis: a worst-case dynamic analysis. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 17245-252. - PubMed
-
- Appay, V., J. R. Almeida, D. Sauce, B. Autran, and L. Papagno. 2007. Accelerated immune senescence and HIV-1 infection. Exp. Gerontol. 42432-437. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner, M., C. A. Ball, J. A. Blake, D. Botstein, H. Butler, J. M. Cherry, A. P. Davis, K. Dolinski, S. S. Dwight, J. T. Eppig, M. A. Harris, D. P. Hill, L. Issel-Tarver, A. Kasarskis, S. Lewis, J. C. Matese, J. E. Richardson, M. Ringwald, G. M. Rubin, G. Sherlock, et al. 2000. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2525-29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Audige, A., M. Urosevic, E. Schlaepfer, R. Walker, D. Powell, S. Hallenberger, H. Joller, H. U. Simon, R. Dummer, and R. F. Speck. 2006. Anti-HIV state but not apoptosis depends on IFN signature in CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 1776227-6237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

