Intestinal alkaline phosphatase detoxifies lipopolysaccharide and prevents inflammation in zebrafish in response to the gut microbiota
- PMID: 18078689
- PMCID: PMC2730374
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2007.10.010
Intestinal alkaline phosphatase detoxifies lipopolysaccharide and prevents inflammation in zebrafish in response to the gut microbiota
Abstract
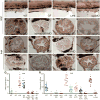
Vertebrates harbor abundant lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in their gut microbiota. Alkaline phosphatases can dephosphorylate and detoxify the endotoxin component of LPS. Here, we show that expression of the zebrafish intestinal alkaline phosphatase (Iap), localized to the intestinal lumen brush border, is induced during establishment of the gut microbiota. Iap-deficient zebrafish are hypersensitive to LPS toxicity and exhibit the excessive intestinal neutrophil influx characteristic of wild-type zebrafish exposed to LPS. Both of these Iap mutant phenotypes are dependent on Myd88 and Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor (Tnfr), proteins also involved in LPS sensitivity in mammals. When reared germ-free, the intestines of Iap-deficient zebrafish are devoid of neutrophils. Together, these findings demonstrate that the endogenous microbiota establish the normal homeostatic level of neutrophils in the zebrafish intestine through a process involving Iap, Myd88, and Tnfr. Thus, by preventing inflammatory responses, Iap plays a crucial role in promoting mucosal tolerance to resident gut bacteria.
Figures



Comment in
-
Alkaline phosphatase: keeping the peace at the gut epithelial surface.Cell Host Microbe. 2007 Dec 13;2(6):365-7. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2007.11.004. Cell Host Microbe. 2007. PMID: 18078687 Review.
References
-
- Alpers DH, Zhang Y, Ahnen DJ. Synthesis and parallel secretion of rat intestinal alkaline phosphatase and a surfactant-like particle protein. The American journal of physiology. 1995;268:E1205–1214. - PubMed
-
- Bates JM, Mittge E, Kuhlman J, Baden KN, Cheesman SE, Guillemin K. Distinct signals from the microbiota promote different aspects of zebrafish gut differentiation. Developmental biology. 2006;297:374–386. - PubMed
-
- Bennett CM, Kanki JP, Rhodes J, Liu TX, Paw BH, Kieran MW, Langenau DM, Delahaye-Brown A, Zon LI, Fleming MD, et al. Myelopoiesis in the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Blood. 2001;98:643–651. - PubMed
-
- Berczi I, Bertok L, Bereznai T. Comparative studies on the toxicity of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide endotoxin in various animal species. Canadian journal of microbiology. 1966;12:1070–1071. - PubMed
-
- Beumer C, Wulferink M, Raaben W, Fiechter D, Brands R, Seinen W. Calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase, a novel therapeutic drug for lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated diseases, attenuates LPS toxicity in mice and piglets. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 2003;307:737–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

