The deacetylase HDAC6 is a novel critical component of stress granules involved in the stress response
- PMID: 18079183
- PMCID: PMC2113037
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.461107
The deacetylase HDAC6 is a novel critical component of stress granules involved in the stress response
Abstract
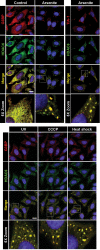
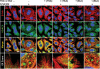
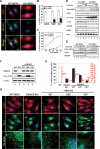
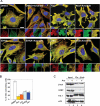
An essential part of the cellular response to environmental stress is a reversible translational suppression, taking place in dynamic cytoplasmic structures called stress granules (SGs). We discovered that HDAC6, a cytoplasmic deacetylase that acts on tubulin and HSP90 and also binds ubiquitinated proteins with high affinity, is a novel critical SG component. We found that HDAC6 interacts with another SG protein, G3BP (Ras-GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein 1), and localizes to SGs under all stress conditions tested. We show that pharmacological inhibition or genetic ablation of HDAC6 abolishes SG formation. Intriguingly, we found that the ubiquitin-binding domain of HDAC6 is essential and that SGs are strongly positive for ubiquitin. Moreover, disruption of microtubule arrays or impairment of motor proteins also prevents formation of SGs. These findings identify HDAC6 as a central component of the stress response, and suggest that it coordinates the formation of SGs by mediating the motor-protein-driven movement of individual SG components along microtubules.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson P., Kedersha N., Kedersha N. Stressful initiations. J. Cell Sci. 2002;115:3227–3234. - PubMed
-
- Bali P., Pranpat M., Bradner J., Balasis M., Fiskus W., Guo F., Rocha K., Kumaraswamy S., Boyapalle S., Atadja P., Pranpat M., Bradner J., Balasis M., Fiskus W., Guo F., Rocha K., Kumaraswamy S., Boyapalle S., Atadja P., Bradner J., Balasis M., Fiskus W., Guo F., Rocha K., Kumaraswamy S., Boyapalle S., Atadja P., Balasis M., Fiskus W., Guo F., Rocha K., Kumaraswamy S., Boyapalle S., Atadja P., Fiskus W., Guo F., Rocha K., Kumaraswamy S., Boyapalle S., Atadja P., Guo F., Rocha K., Kumaraswamy S., Boyapalle S., Atadja P., Rocha K., Kumaraswamy S., Boyapalle S., Atadja P., Kumaraswamy S., Boyapalle S., Atadja P., Boyapalle S., Atadja P., Atadja P., et al. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: A novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:26729–26734. - PubMed
-
- Bertolotti A., Zhang Y., Hendershot L.M., Harding H.P., Ron D., Zhang Y., Hendershot L.M., Harding H.P., Ron D., Hendershot L.M., Harding H.P., Ron D., Harding H.P., Ron D., Ron D. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000;2:326–332. - PubMed
-
- Bertos N.R., Gilquin B., Chan G.K., Yen T.J., Khochbin S., Yang X.J., Gilquin B., Chan G.K., Yen T.J., Khochbin S., Yang X.J., Chan G.K., Yen T.J., Khochbin S., Yang X.J., Yen T.J., Khochbin S., Yang X.J., Khochbin S., Yang X.J., Yang X.J. Role of the tetradecapeptide repeat domain of human histone deacetylase 6 in cytoplasmic retention. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:48246–48254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
