Serine-7 of the RNA polymerase II CTD is specifically required for snRNA gene expression
- PMID: 18079403
- PMCID: PMC2263945
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1145989
Serine-7 of the RNA polymerase II CTD is specifically required for snRNA gene expression
Abstract
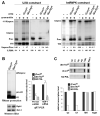
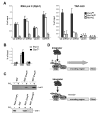
RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcribes genes that encode proteins and noncoding small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). The carboxyl-terminal repeat domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of mammalian RNA Pol II, comprising tandem repeats of the heptapeptide consensus Tyr1-Ser2-Pro3-Thr4-Ser5-Pro6-Ser7, is required for expression of both gene types. We show that mutation of serine-7 to alanine causes a specific defect in snRNA gene expression. We also present evidence that phosphorylation of serine-7 facilitates interaction with the snRNA gene-specific Integrator complex. These findings assign a biological function to this amino acid and highlight a gene type-specific requirement for a residue within the CTD heptapeptide, supporting the existence of a CTD code.
Figures
Comment in
-
Transcription. Seven ups the code.Science. 2007 Dec 14;318(5857):1735-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1152624. Science. 2007. PMID: 18079391 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

