A critical role of RICK/RIP2 polyubiquitination in Nod-induced NF-kappaB activation
- PMID: 18079694
- PMCID: PMC2234345
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601962
A critical role of RICK/RIP2 polyubiquitination in Nod-induced NF-kappaB activation
Abstract
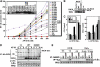
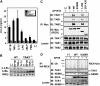
Nod1 and Nod2 are intracellular proteins that are involved in host recognition of specific bacterial molecules and are genetically associated with several inflammatory diseases. Nod1 and Nod2 stimulation activates NF-kappaB through RICK, a caspase-recruitment domain-containing kinase. However, the mechanism by which RICK activates NF-kappaB in response to Nod1 and Nod2 stimulation is unknown. Here we show that RICK is conjugated with lysine-63-linked polyubiquitin chains at lysine 209 (K209) located in its kinase domain upon Nod1 or Nod2 stimulation and by induced oligomerization of RICK. Polyubiquitination of RICK at K209 was essential for RICK-mediated IKK activation and cytokine/chemokine secretion. However, RICK polyubiquitination did not require the kinase activity of RICK or alter the interaction of RICK with NEMO, a regulatory subunit of IkappaB kinase (IKK). Instead, polyubiquitination of RICK was found to mediate the recruitment of TAK1, a kinase that was found to be essential for Nod1-induced signaling. Thus, RICK polyubiquitination links TAK1 to IKK complexes, a critical step in Nod1/Nod2-mediated NF-kappaB activation.
Figures




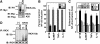

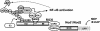
References
-
- Abbott DW, Wilkins A, Asara JM, Cantley LC (2004) The Crohn's disease protein, NOD2, requires RIP2 in order to induce ubiquitinylation of a novel site on NEMO. Curr Biol 14: 2217–2227 - PubMed
-
- Boone DL, Turer EE, Lee EG, Ahmad RC, Wheeler MT, Tsui C, Hurley P, Chien M, Chai S, Hitotsumatsu O, McNally E, Pickart C, Ma A (2004) The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat Immunol 5: 1052–1060 - PubMed
-
- Boughan PK, Argent RH, Body-Malapel M, Park JH, Ewings KE, Bowie AG, Ong SJ, Cook SJ, Sorensen OE, Manzo BA, Inohara N, Klein NJ, Nunez G, Atherton JC, Bajaj-Elliott M (2006) Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-1 and epidermal growth factor receptor: critical regulators of beta-defensins during Helicobacter pylori infection. J Biol Chem 281: 11637–11648 - PubMed
-
- Chamaillard M, Hashimoto M, Horie Y, Masumoto J, Qiu S, Saab L, Ogura Y, Kawasaki A, Fukase K, Kusumoto S, Valvano MA, Foster SJ, Mak TW, Nunez G, Inohara N (2003) An essential role for NOD1 in host recognition of bacterial peptidoglycan containing diaminopimelic acid. Nat Immunol 4: 702–707 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

