Anemia is a common but neglected complication of adjuvant chemotherapy for early breast cancer
- PMID: 18080014
- PMCID: PMC2133099
- DOI: 10.3747/co.2007.156
Anemia is a common but neglected complication of adjuvant chemotherapy for early breast cancer
Abstract
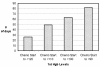
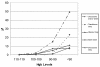
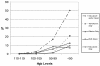
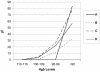
In this study, we set out to determine the frequency and severity of anemia and the corrective interventions used during adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer.We conducted a retrospective electronic chart review of 702 patients who received adjuvant breast cancer chemotherapy at four BC Cancer Agency centres in 2002 and 2003. For these patients, we recorded the initial hemoglobin reading and the date of the first hemoglobin reading in the ranges 110-119 g/L, 100-109 g/L, 90-99 g/L, and <90 g/L. We also recorded any discussion about, or delivery of, interventions for anemia [transfusion, epoetin (epo) or both].Median age of the study population was 51 years, and it varied with chemotherapy type. Among the patients, 12% had a hemoglobin reading <120 g/L before the start of chemotherapy. Overall, the proportion of patients with at least one hemoglobin reading <120 g/L was 78%; <110 g/L, 54%; <100 g/L, 31%; and <90 g/L, 14%. Depending on chemotherapy type, a hemoglobin reading <100 g/L occurred in 5% to 54% of patients. Intervention rates increased as hemoglobin declined. For 99 patients with a hemoglobin reading <90 g/L, a discussion of anemia was documented in the treatment chart in 49% of cases, a transfusion was delivered in 23%, epo was used in 11%, and transfusion and epo were both delivered in 5%.Anemia was relatively common and varied with chemotherapy type. Documentation of a discussion of anemia occurred in fewer than 20% of the patients with a hemoglobin reading of 90-99 g/L and in only half the patients with a hemoglobin reading <90 g/L. Intervention rates were low at hemoglobin readings for which randomized trials have shown that intervention can improve quality of life.
Keywords: Anemia; breast cancer; chemotherapy; epoetin; transfusion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Population-based analysis of the frequency of anemia and its management before and during chemotherapy in patients with malignant lymphoma.Am J Clin Oncol. 2010 Oct;33(5):465-8. doi: 10.1097/COC.0b013e3181b4b147. Am J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19935386
-
Impact of Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) and Epoetin (EPO) on Hematologic Toxicities and Quality of Life in Patients During Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Early Breast Cancer: Results From the Multi-Center Randomized ADEBAR Trial.Clin Breast Cancer. 2020 Dec;20(6):439-447. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.03.008. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Clin Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32800493 Clinical Trial.
-
Weekly epoetin alfa during adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: effect on hemoglobin levels and quality of life.Clin Breast Cancer. 2005 Jun;6(2):132-42. doi: 10.3816/cbc.2005.n.015. Clin Breast Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16001991 Clinical Trial.
-
The blue cross blue shield assessment technology review: summary of findings.Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2005;18(3):423-31. doi: 10.1016/j.beha.2005.01.019. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2005. PMID: 15792916 Review.
-
Epoetin treatment of anemia associated with cancer therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001 Aug 15;93(16):1204-14. doi: 10.1093/jnci/93.16.1204. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001. PMID: 11504766
Cited by
-
Real-world data on neoadjuvant chemotherapy with dual-anti HER2 therapy in HER2 positive breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jan 25;24(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-11871-0. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38273267 Free PMC article.
-
Anaemia and pathologic complete response rate according to carboplatin dose in HER2+ breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant TCHP.Cancer Med. 2023 Jan;12(2):1409-1417. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5022. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 35837812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Groopman JE, Itri LM. Chemotherapy-induced anemia in adults: incidence and treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999;91:1616–34. - PubMed
-
- Ray–Coquard I, Le Cesne A, Rubio MT, et al. Risk model for severe anemia requiring red blood cell transfusion after cytotoxic conventional chemotherapy regimens. The Elypse 1 Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2840–6. - PubMed
-
- Dranitsaris G, Clemons M, Verma S, Lau C, Vincent M. Chemotherapy-induced anaemia during adjuvant treatment for breast cancer: development of a prediction model. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:856–63. - PubMed
-
- Seshadri T, Prince HM, Bell DR, et al. for the Australian Cancer Anaemia Study Group. The Australian Cancer Anaemia Survey: a snapshot of anaemia in adult patients with cancer. Med J Aust. 2005;182:453–7. - PubMed
-
- Barrett–Lee P, Bokemeyer C, Gascon P, et al. Management of cancer-related anemia in patients with breast or gynecologic cancer: new insights based on results from the European Cancer Anemia Survey. Oncologist. 2005;10:743–57. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

