Hyperammonemic encephalopathy caused by carnitine deficiency
- PMID: 18080167
- PMCID: PMC2359173
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-007-0473-0
Hyperammonemic encephalopathy caused by carnitine deficiency
Abstract
Carnitine is an essential co-factor in fatty acid metabolism. Carnitine deficiency can impair fatty acid oxidation, rarely leading to hyperammonemia and encephalopathy. We present the case of a 35-year-old woman who developed acute mental status changes, asterixis, and diffuse muscle weakness. Her ammonia level was elevated at 276 microg/dL. Traditional ammonia-reducing therapies were initiated, but proved ineffective. Pharmacologic, microbial, and autoimmune causes for the hyperammonemia were excluded. The patient was severely malnourished and her carnitine level was found to be extremely low. After carnitine supplementation, ammonia levels normalized and the patient's mental status returned to baseline. In the setting of refractory hyperammonemia, this case illustrates how careful investigation may reveal a treatable condition.
Figures
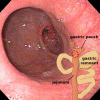
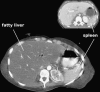
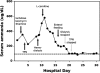
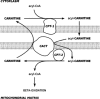
References
-
- Di Donato S, Pelucchetti D, Rimoldi M, et al. Systemic carnitine deficiency: clinical, biochemical, and morphological cure with L-carnitine. Neurology. 1984;34:157–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

