Environmental novelty is signaled by reduction of the hippocampal theta frequency
- PMID: 18081172
- PMCID: PMC2678674
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.20394
Environmental novelty is signaled by reduction of the hippocampal theta frequency
Abstract
The hippocampal formation (HF) plays a key role in novelty detection, but the mechanisms remain unknown. Novelty detection aids the encoding of new information into memory-a process thought to depend on the HF and to be modulated by the theta rhythm of EEG. We examined EEG recorded in the HF of rats foraging for food within a novel environment, as it became familiar over the next five days, and in two more novel environments unexpectedly experienced in trials interspersed with familiar trials over three further days. We found that environmental novelty produces a sharp reduction in the theta frequency of foraging rats, that this reduction is greater for an unexpected environment than for a completely novel one, and that it slowly disappears with increasing familiarity. These results do not reflect changes in running speed and suggest that the septo-hippocampal system signals unexpected environmental change via a reduction in theta frequency. In addition, they provide evidence in support of a cholinergically mediated mechanism for novelty detection, have important implications for our understanding of oscillatory coding within memory and for the interpretation of event-related potentials, and provide indirect support for the oscillatory interference model of grid cell firing in medial entorhinal cortex.
(c) 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
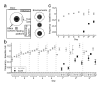
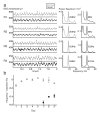

Comment in
-
Hippocampal theta frequency and novelty.Hippocampus. 2009 Apr;19(4):407-8; author reply 409-10. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20541. Hippocampus. 2009. PMID: 19212942 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Synergy of direct and indirect cholinergic septo-hippocampal pathways coordinates firing in hippocampal networks.J Neurosci. 2015 Jun 3;35(22):8394-410. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4460-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26041909 Free PMC article.
-
Mode shifting between storage and recall based on novelty detection in oscillating hippocampal circuits.Hippocampus. 2004;14(6):722-41. doi: 10.1002/hipo.10214. Hippocampus. 2004. PMID: 15318331
-
Modulating medial septal cholinergic activity reduces medial entorhinal theta frequency without affecting speed or grid coding.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 6;7(1):14573. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15100-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29109512 Free PMC article.
-
The theta/gamma discrete phase code occuring during the hippocampal phase precession may be a more general brain coding scheme.Hippocampus. 2005;15(7):913-22. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20121. Hippocampus. 2005. PMID: 16161035 Review.
-
Timing and hippocampal theta in animals.Rev Neurosci. 2006;17(1-2):157-62. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2006.17.1-2.157. Rev Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16703949 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in Search Path Complexity and Length During Learning of a Virtual Water Maze: Age Differences and Differential Associations with Hippocampal Subfield Volumes.Cereb Cortex. 2016 Jun;26(6):2391-401. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhv061. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Cereb Cortex. 2016. PMID: 25838036 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociation between the experience-dependent development of hippocampal theta sequences and single-trial phase precession.J Neurosci. 2015 Mar 25;35(12):4890-902. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2614-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25810520 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal fibroblast growth factor treatment enhances cocaine sensitization.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012 Nov;103(1):6-17. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2012.07.006. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012. PMID: 22819969 Free PMC article.
-
Neurophysiological correlates of object recognition in the dorsal subiculum.Front Behav Neurosci. 2012 Jul 19;6:46. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2012.00046. eCollection 2012. Front Behav Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22833721 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic θ Frequency Coordination within and between the Prefrontal Cortex-Hippocampus Circuit during Learning of a Spatial Avoidance Task.eNeuro. 2022 Apr 21;9(2):ENEURO.0414-21.2022. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0414-21.2022. Print 2022 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 35396256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggleton JP, Brown MW. Episodic memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal-anterior thalamic axis. Behavioural Brain Sci. 1999;22:425–490. - PubMed
-
- Axmacher N, Mormann F, Fernandez G, Elger CE, Fell J. Memory formation by neuronal synchronization. Brain Res.Rev. 2006;52:170–182. - PubMed
-
- Borisyuk R, Denham M, Hoppensteadt F, Kazanovich Y, Vinogradova O. Oscillatory model of novelty detection. Network. 2001;12:1–20. - PubMed
-
- Bostock E, Muller RU, Kubie JL. Experience-dependent modifications of hippocampal place cell firing. Hippocampus. 1991;1:193–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

